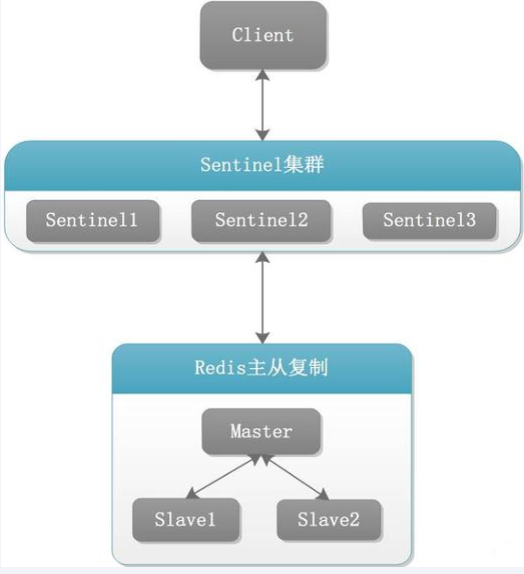
哨兵(sentinel)&集群(cluster)
哨兵(sentinel)
吹哨人巡查监控后台master主机是否故障,如果故障了根据投票数自动将某一个从库转换为新主库,继续对外服务
作用
- 监控redis运行状态,包括master和slave
- 当master down机,能自动将slave切换成新master
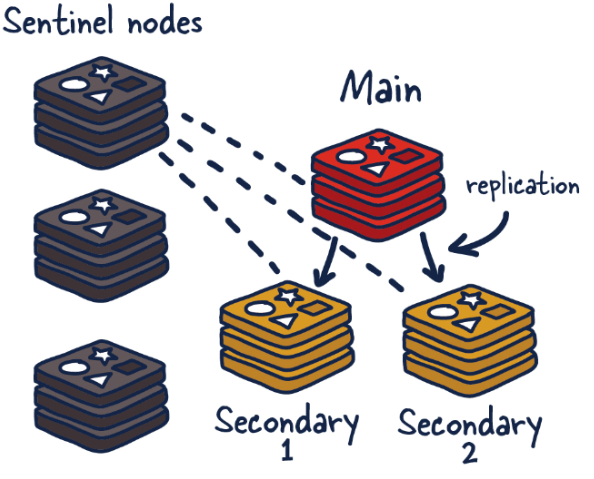
Redis Sentinel是Redis 的高可用性解决方案,由一个或多个Sentinel(哨兵)实例组成。它可以监视任意多个主服务器,以及这些主服务器属下的所有从服务器,并在被监视的主服务器进入下线状态时,自动将下线主服务器属下的某个从服务器升级为新的主服务器,它的主要功能如下:
主从监控
Sentinel会不断地检查你的主服务器和从服务器是否运作正常。
消息通知
当被监控的某个 Redis 服务器出现问题时, Sentinel可以通过API向管理员或者其他应用程序发送通知。
故障转移
如果master异常,则会进行主从切换,将其中一个slave作为新master,当主服务器不能正常工作时,Sentinel会自动进行故障迁移,也就是主从切换。
配置中心
客户端通过连接哨兵来获得当前redis服务的主节点地址
哨兵原理
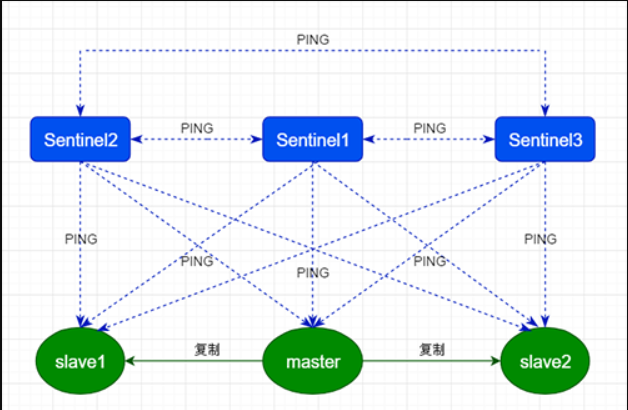
Sentinel 使用的算法核心是 Raft 算法,主要用途就是用于分布式系统,系统容错,以及Leader选举,每个Sentinel都需要定期的执行以下任务:
- 每个 Sentinel 会自动发现其他 Sentinel 和从服务器,它以每秒钟一次的频率向它所知的主服务器、从服务器以及其他 Sentinel 实例发送一个 PING 命令。
- 如果一个实例(instance)距离最后一次有效回复 PING 命令的时间超过 down-after-milliseconds 选项所指定的值, 那么这个实例会被 Sentinel 标记为主观下线。 有效回复可以是: +PONG 、 -LOADING 或者 -MASTERDOWN 。
- 如果一个主服务器被标记为主观下线, 那么正在监视这个主服务器的所有Sentinel要以每秒一次的频率确认主服务器的确进入了主观下线状态。
- 如果一个主服务器被标记为主观下线, 并且有足够数量的Sentinel(至少要达到配置文件指定的数量)在指定的时间范围内同意这一判断, 那么这个主服务器被标记为客观下线。
- 在一般情况下, 每个Sentinel会以每 10 秒一次的频率向它已知的所有主服务器和从服务器发送 INFO 命令。 当一个主服务器被Sentinel标记为客观下线时,Sentinel向下线主服务器的所有从服务器发送 INFO 命令的频率会从 10 秒一次改为每秒一次。
- 当没有足够数量的Sentinel同意主服务器已经下线, 主服务器的客观下线状态就会被移除。 当主服务器重新向Sentinel的 PING 命令返回有效回复时, 主服务器的主管下线状态就会被移除.
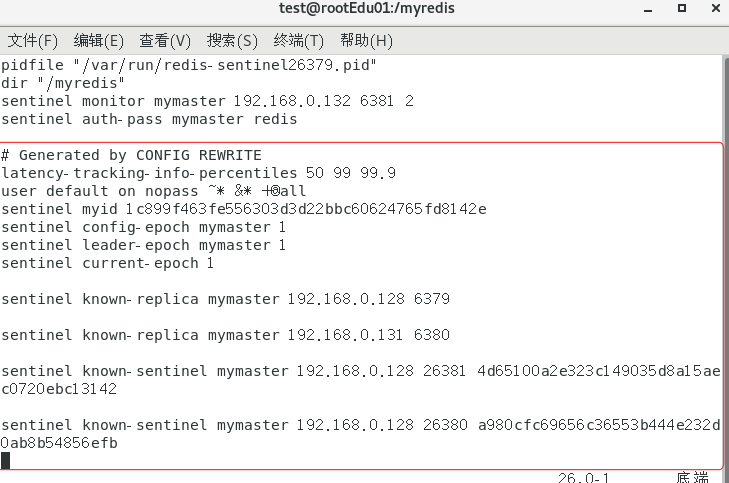
sentinel配置文件
# 哨兵sentinel实例运行的端口,默认26379
port 26379
# 是否设置为后台启动。
daemonize no
#pid文件地址
pidfile /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid
#日志文件地址
logfile ""
# 指定sentinel工作目录
dir /tmp
# 哨兵sentinel监控的redis主节点的
## ip:主机ip地址
## port:哨兵端口号
## master-name:可以自己命名的主节点名字(只能由字母A-z、数字0-9 、这三个字符".-_"组成。)
## quorum:当这些quorum个数sentinel哨兵认为master主节点失联 那么这时 客观上认为主节点失联了
# sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum>
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2
# 指定主节点应答哨兵sentinel的最大时间间隔,超过这个时间,哨兵主观上认为主节点下线,默认30秒
# sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
acllog-max-len 128
# 指定了在发生failover主备切换时,最多可以有多少个slave同时对新的master进行同步。这个数字越小,完成failover所需的时间就越长;反之,但是如果这个数字越大,就意味着越多的slave因为replication而不可用。可以通过将这个值设为1,来保证每次只有一个slave,处于不能处理命令请求的状态。
# sentinel parallel-syncs <master-name> <numslaves>
sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1
# 故障转移的超时时间failover-timeout,默认三分钟,可以用在以下这些方面:
## 1. 同一个sentinel对同一个master两次failover之间的间隔时间。
## 2. 当一个slave从一个错误的master那里同步数据时开始,直到slave被纠正为从正确的master那里同步数据时结束。
## 3. 当想要取消一个正在进行的failover时所需要的时间。
## 4.当进行failover时,配置所有slaves指向新的master所需的最大时间。不过,即使过了这个超时,slaves依然会被正确配置为指向master,但是就不按parallel-syncs所配置的规则来同步数据了
# sentinel failover-timeout <master-name> <milliseconds>
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000
sentinel deny-scripts-reconfig yes
SENTINEL resolve-hostnames no
SENTINEL announce-hostnames no重点参数
bind
服务监听地址,用于客户端连接,默认本机地址
daemonize
是否以后台damon方式运行
protected-mode
安全保护模式
port
端口
logfile
日志文件路径
pidfile
pid文件路径
dir
工作目录
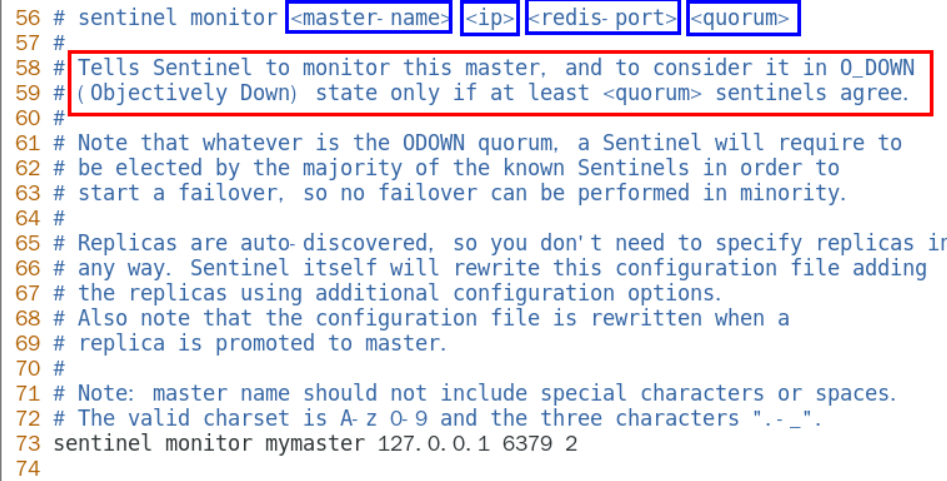
sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum>
- 设置要监控的master服务器
- quorum表示最少有几个哨兵认可客观下线,同意故障迁移的法定票数。
sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>
master设置了密码,连接master服务的密码
其他参数(默认就行)
sentinel down-after-milliseconds <master-name> <milliseconds>:
指定多少毫秒之后,主节点没有应答哨兵,此时哨兵主观上认为主节点下线
sentinel parallel-syncs <master-name> <nums>:
表示允许并行同步的slave个数,当Master挂了后,哨兵会选出新的Master,此时,剩余的slave会向新的master发起同步数据
sentinel failover-timeout <master-name> <milliseconds>:
故障转移的超时时间,进行故障转移时,如果超过设置的毫秒,表示故障转移失败
sentinel notification-script <master-name> <script-path> :
配置当某一事件发生时所需要执行的脚本
sentinel client-reconfig-script <master-name> <script-path>:
客户端重新配置主节点参数脚本
示例:
三个哨兵实例需要三台虚拟机,考虑到机器性能有限,这里将三个哨兵实例配置到一台虚拟机上,配置三份不同的哨兵配置文件即可:sentinel26379.conf、sentinel26380.conf、sentinel26381.conf,将它们存放到/myredis下。
/myredi目录下新建或者拷贝sentinel.conf文件,名字不能错,如果没有则新建文件
sentinel.conf文件
# Example sentinel.conf
# By default protected mode is disabled in sentinel mode. Sentinel is reachable
# from interfaces different than localhost. Make sure the sentinel instance is
# protected from the outside world via firewalling or other means.
protected-mode no
# port <sentinel-port>
# The port that this sentinel instance will run on
port 26379
# By default Redis Sentinel does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it.
# Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid when
# daemonized.
daemonize no
# When running daemonized, Redis Sentinel writes a pid file in
# /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid by default. You can specify a custom pid file
# location here.
pidfile /var/run/redis-sentinel.pid
# Specify the server verbosity level.
# This can be one of:
# debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing)
# verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level)
# notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably)
# warning (only very important / critical messages are logged)
# nothing (nothing is logged)
loglevel notice
# Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force
# Sentinel to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard
# output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null
logfile ""
# To enable logging to the system logger, just set 'syslog-enabled' to yes,
# and optionally update the other syslog parameters to suit your needs.
# syslog-enabled no
# Specify the syslog identity.
# syslog-ident sentinel
# Specify the syslog facility. Must be USER or between LOCAL0-LOCAL7.
# syslog-facility local0
# sentinel announce-ip <ip>
# sentinel announce-port <port>
#
# The above two configuration directives are useful in environments where,
# because of NAT, Sentinel is reachable from outside via a non-local address.
#
# When announce-ip is provided, the Sentinel will claim the specified IP address
# in HELLO messages used to gossip its presence, instead of auto-detecting the
# local address as it usually does.
#
# Similarly when announce-port is provided and is valid and non-zero, Sentinel
# will announce the specified TCP port.
#
# The two options don't need to be used together, if only announce-ip is
# provided, the Sentinel will announce the specified IP and the server port
# as specified by the "port" option. If only announce-port is provided, the
# Sentinel will announce the auto-detected local IP and the specified port.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel announce-ip 1.2.3.4
# dir <working-directory>
# Every long running process should have a well-defined working directory.
# For Redis Sentinel to chdir to /tmp at startup is the simplest thing
# for the process to don't interfere with administrative tasks such as
# unmounting filesystems.
dir /tmp
# sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum>
#
# Tells Sentinel to monitor this master, and to consider it in O_DOWN
# (Objectively Down) state only if at least <quorum> sentinels agree.
#
# Note that whatever is the ODOWN quorum, a Sentinel will require to
# be elected by the majority of the known Sentinels in order to
# start a failover, so no failover can be performed in minority.
#
# Replicas are auto-discovered, so you don't need to specify replicas in
# any way. Sentinel itself will rewrite this configuration file adding
# the replicas using additional configuration options.
# Also note that the configuration file is rewritten when a
# replica is promoted to master.
#
# Note: master name should not include special characters or spaces.
# The valid charset is A-z 0-9 and the three characters ".-_".
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2
# sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>
#
# Set the password to use to authenticate with the master and replicas.
# Useful if there is a password set in the Redis instances to monitor.
#
# Note that the master password is also used for replicas, so it is not
# possible to set a different password in masters and replicas instances
# if you want to be able to monitor these instances with Sentinel.
#
# However you can have Redis instances without the authentication enabled
# mixed with Redis instances requiring the authentication (as long as the
# password set is the same for all the instances requiring the password) as
# the AUTH command will have no effect in Redis instances with authentication
# switched off.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel auth-pass mymaster MySUPER--secret-0123passw0rd
# sentinel auth-user <master-name> <username>
#
# This is useful in order to authenticate to instances having ACL capabilities,
# that is, running Redis 6.0 or greater. When just auth-pass is provided the
# Sentinel instance will authenticate to Redis using the old "AUTH <pass>"
# method. When also an username is provided, it will use "AUTH <user> <pass>".
# In the Redis servers side, the ACL to provide just minimal access to
# Sentinel instances, should be configured along the following lines:
#
# user sentinel-user >somepassword +client +subscribe +publish \
# +ping +info +multi +slaveof +config +client +exec on
# sentinel down-after-milliseconds <master-name> <milliseconds>
#
# Number of milliseconds the master (or any attached replica or sentinel) should
# be unreachable (as in, not acceptable reply to PING, continuously, for the
# specified period) in order to consider it in S_DOWN state (Subjectively
# Down).
#
# Default is 30 seconds.
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
# IMPORTANT NOTE: starting with Redis 6.2 ACL capability is supported for
# Sentinel mode, please refer to the Redis website https://redis.io/topics/acl
# for more details.
# Sentinel's ACL users are defined in the following format:
#
# user <username> ... acl rules ...
#
# For example:
#
# user worker +@admin +@connection ~* on >ffa9203c493aa99
#
# For more information about ACL configuration please refer to the Redis
# website at https://redis.io/topics/acl and redis server configuration
# template redis.conf.
# ACL LOG
#
# The ACL Log tracks failed commands and authentication events associated
# with ACLs. The ACL Log is useful to troubleshoot failed commands blocked
# by ACLs. The ACL Log is stored in memory. You can reclaim memory with
# ACL LOG RESET. Define the maximum entry length of the ACL Log below.
acllog-max-len 128
# Using an external ACL file
#
# Instead of configuring users here in this file, it is possible to use
# a stand-alone file just listing users. The two methods cannot be mixed:
# if you configure users here and at the same time you activate the external
# ACL file, the server will refuse to start.
#
# The format of the external ACL user file is exactly the same as the
# format that is used inside redis.conf to describe users.
#
# aclfile /etc/redis/sentinel-users.acl
# requirepass <password>
#
# You can configure Sentinel itself to require a password, however when doing
# so Sentinel will try to authenticate with the same password to all the
# other Sentinels. So you need to configure all your Sentinels in a given
# group with the same "requirepass" password. Check the following documentation
# for more info: https://redis.io/topics/sentinel
#
# IMPORTANT NOTE: starting with Redis 6.2 "requirepass" is a compatibility
# layer on top of the ACL system. The option effect will be just setting
# the password for the default user. Clients will still authenticate using
# AUTH <password> as usually, or more explicitly with AUTH default <password>
# if they follow the new protocol: both will work.
#
# New config files are advised to use separate authentication control for
# incoming connections (via ACL), and for outgoing connections (via
# sentinel-user and sentinel-pass)
#
# The requirepass is not compatible with aclfile option and the ACL LOAD
# command, these will cause requirepass to be ignored.
# sentinel sentinel-user <username>
#
# You can configure Sentinel to authenticate with other Sentinels with specific
# user name.
# sentinel sentinel-pass <password>
#
# The password for Sentinel to authenticate with other Sentinels. If sentinel-user
# is not configured, Sentinel will use 'default' user with sentinel-pass to authenticate.
# sentinel parallel-syncs <master-name> <numreplicas>
#
# How many replicas we can reconfigure to point to the new replica simultaneously
# during the failover. Use a low number if you use the replicas to serve query
# to avoid that all the replicas will be unreachable at about the same
# time while performing the synchronization with the master.
sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1
# sentinel failover-timeout <master-name> <milliseconds>
#
# Specifies the failover timeout in milliseconds. It is used in many ways:
#
# - The time needed to re-start a failover after a previous failover was
# already tried against the same master by a given Sentinel, is two
# times the failover timeout.
#
# - The time needed for a replica replicating to a wrong master according
# to a Sentinel current configuration, to be forced to replicate
# with the right master, is exactly the failover timeout (counting since
# the moment a Sentinel detected the misconfiguration).
#
# - The time needed to cancel a failover that is already in progress but
# did not produced any configuration change (SLAVEOF NO ONE yet not
# acknowledged by the promoted replica).
#
# - The maximum time a failover in progress waits for all the replicas to be
# reconfigured as replicas of the new master. However even after this time
# the replicas will be reconfigured by the Sentinels anyway, but not with
# the exact parallel-syncs progression as specified.
#
# Default is 3 minutes.
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000
# SCRIPTS EXECUTION
#
# sentinel notification-script and sentinel reconfig-script are used in order
# to configure scripts that are called to notify the system administrator
# or to reconfigure clients after a failover. The scripts are executed
# with the following rules for error handling:
#
# If script exits with "1" the execution is retried later (up to a maximum
# number of times currently set to 10).
#
# If script exits with "2" (or an higher value) the script execution is
# not retried.
#
# If script terminates because it receives a signal the behavior is the same
# as exit code 1.
#
# A script has a maximum running time of 60 seconds. After this limit is
# reached the script is terminated with a SIGKILL and the execution retried.
# NOTIFICATION SCRIPT
#
# sentinel notification-script <master-name> <script-path>
#
# Call the specified notification script for any sentinel event that is
# generated in the WARNING level (for instance -sdown, -odown, and so forth).
# This script should notify the system administrator via email, SMS, or any
# other messaging system, that there is something wrong with the monitored
# Redis systems.
#
# The script is called with just two arguments: the first is the event type
# and the second the event description.
#
# The script must exist and be executable in order for sentinel to start if
# this option is provided.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel notification-script mymaster /var/redis/notify.sh
# CLIENTS RECONFIGURATION SCRIPT
#
# sentinel client-reconfig-script <master-name> <script-path>
#
# When the master changed because of a failover a script can be called in
# order to perform application-specific tasks to notify the clients that the
# configuration has changed and the master is at a different address.
#
# The following arguments are passed to the script:
#
# <master-name> <role> <state> <from-ip> <from-port> <to-ip> <to-port>
#
# <state> is currently always "start"
# <role> is either "leader" or "observer"
#
# The arguments from-ip, from-port, to-ip, to-port are used to communicate
# the old address of the master and the new address of the elected replica
# (now a master).
#
# This script should be resistant to multiple invocations.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel client-reconfig-script mymaster /var/redis/reconfig.sh
# SECURITY
#
# By default SENTINEL SET will not be able to change the notification-script
# and client-reconfig-script at runtime. This avoids a trivial security issue
# where clients can set the script to anything and trigger a failover in order
# to get the program executed.
sentinel deny-scripts-reconfig yes
# REDIS COMMANDS RENAMING (DEPRECATED)
#
# WARNING: avoid using this option if possible, instead use ACLs.
#
# Sometimes the Redis server has certain commands, that are needed for Sentinel
# to work correctly, renamed to unguessable strings. This is often the case
# of CONFIG and SLAVEOF in the context of providers that provide Redis as
# a service, and don't want the customers to reconfigure the instances outside
# of the administration console.
#
# In such case it is possible to tell Sentinel to use different command names
# instead of the normal ones. For example if the master "mymaster", and the
# associated replicas, have "CONFIG" all renamed to "GUESSME", I could use:
#
# SENTINEL rename-command mymaster CONFIG GUESSME
#
# After such configuration is set, every time Sentinel would use CONFIG it will
# use GUESSME instead. Note that there is no actual need to respect the command
# case, so writing "config guessme" is the same in the example above.
#
# SENTINEL SET can also be used in order to perform this configuration at runtime.
#
# In order to set a command back to its original name (undo the renaming), it
# is possible to just rename a command to itself:
#
# SENTINEL rename-command mymaster CONFIG CONFIG
# HOSTNAMES SUPPORT
#
# Normally Sentinel uses only IP addresses and requires SENTINEL MONITOR
# to specify an IP address. Also, it requires the Redis replica-announce-ip
# keyword to specify only IP addresses.
#
# You may enable hostnames support by enabling resolve-hostnames. Note
# that you must make sure your DNS is configured properly and that DNS
# resolution does not introduce very long delays.
#
SENTINEL resolve-hostnames no
# When resolve-hostnames is enabled, Sentinel still uses IP addresses
# when exposing instances to users, configuration files, etc. If you want
# to retain the hostnames when announced, enable announce-hostnames below.
#
SENTINEL announce-hostnames no
# When master_reboot_down_after_period is set to 0, Sentinel does not fail over
# when receiving a -LOADING response from a master. This was the only supported
# behavior before version 7.0.
#
# Otherwise, Sentinel will use this value as the time (in ms) it is willing to
# accept a -LOADING response after a master has been rebooted, before failing
# over.
SENTINEL master-reboot-down-after-period mymaster 0配置sentinel
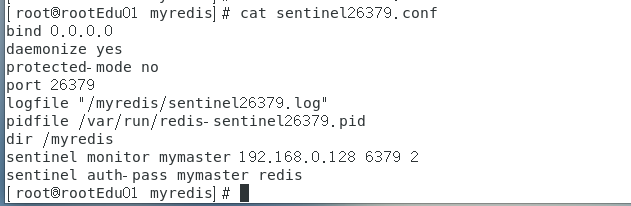
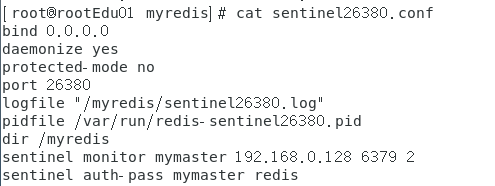
在6379下的/myredis文件夹下创建sentinel26379.conf、sentinel26380.conf、sentinel26381.conf,并写入
bind 0.0.0.0
daemonize yes
protected-mode no
port 26379
logfile "/myredis/sentinel26379.log"
pidfile /var/run/redis-sentinel26379.pid
dir /myredis
sentinel monitor mymaster ip 6379 2 # 2是票数
sentinel auth-pass mymaster redis密码sentinel26379.conf
sentinel26380.conf
sentinel26381.conf
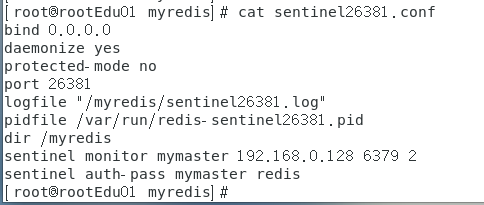
配置主机6379的访问密码
因为我们的6380和6381都配置的主机的访问密码了,所以只配置6379的主机访问密码就可以!
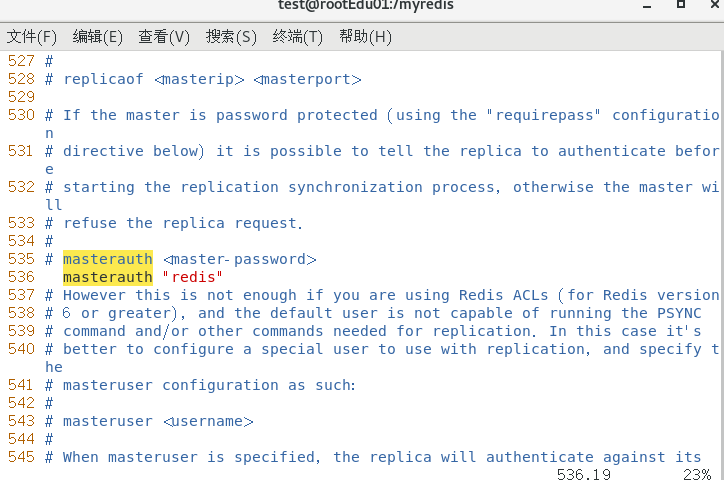
注意:
6379后续可能会变成从机,需要设置访问新主机的密码, 请设置masterauth项访问密码为redis,不然后续可能报错master_link_status:down
启动6379、6380、6381服务
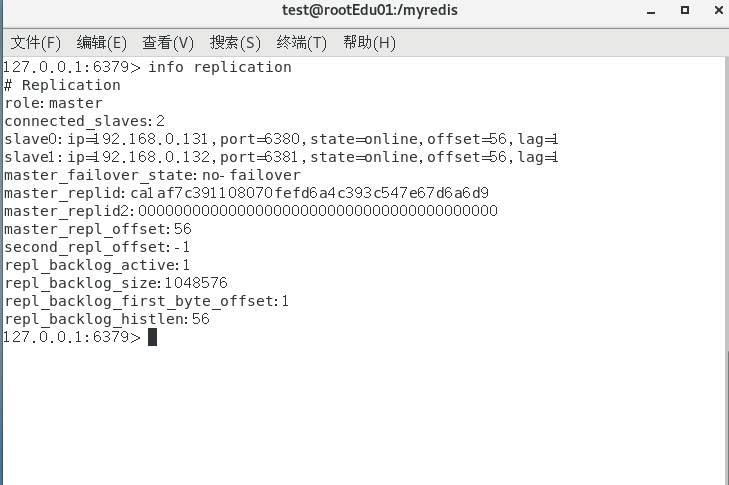
启动sentinel
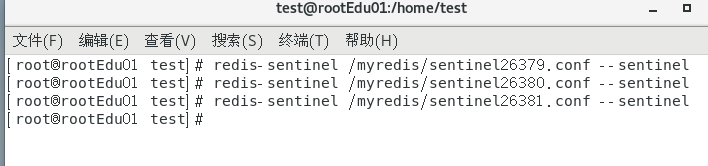
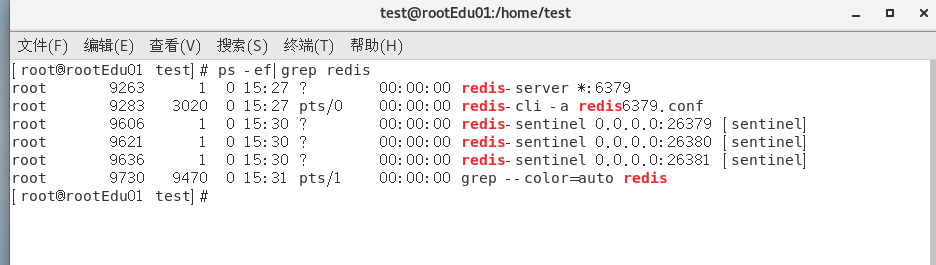
通过redis-sentinel sentinel文件 --sentinel启动
当我们模拟主机挂了,看看从机是否会上位

稍等一下
主机挂了,从机会进行投票,选择一个进行上位
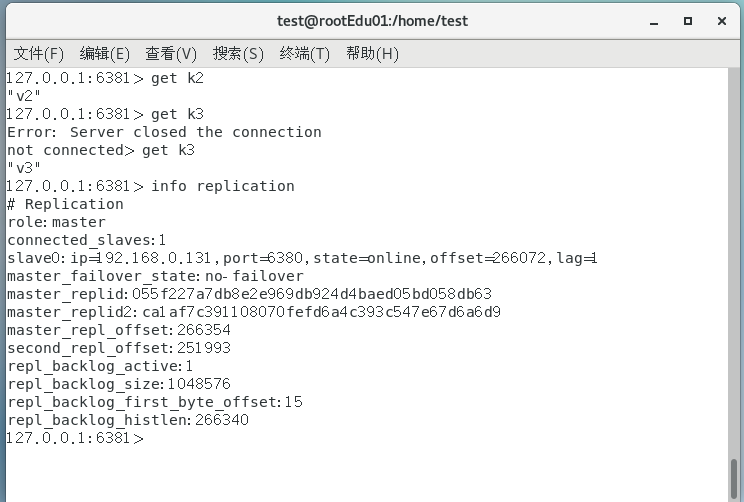
可以看到我们的6381已经上位了,当我们打开6379.log文件查看
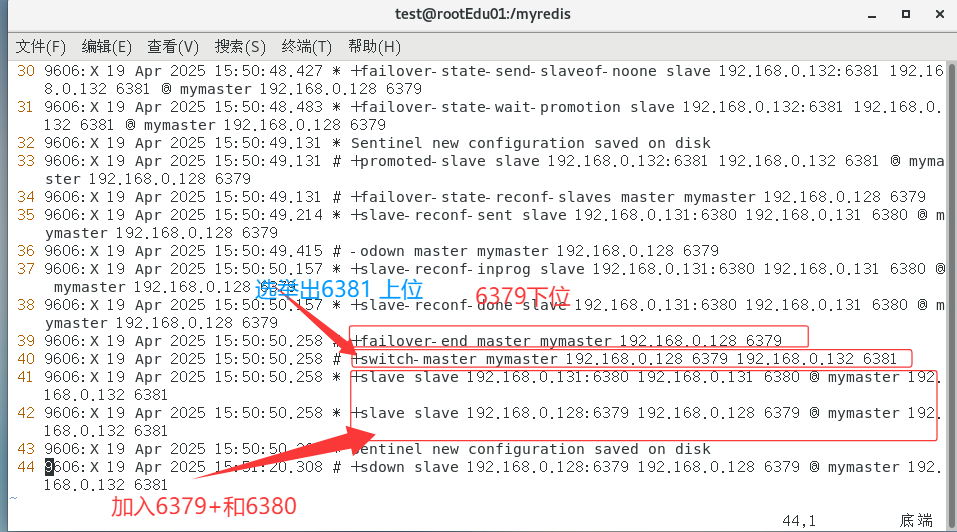
我们的6379没启动,可以看出6379已经不是master变成slave了
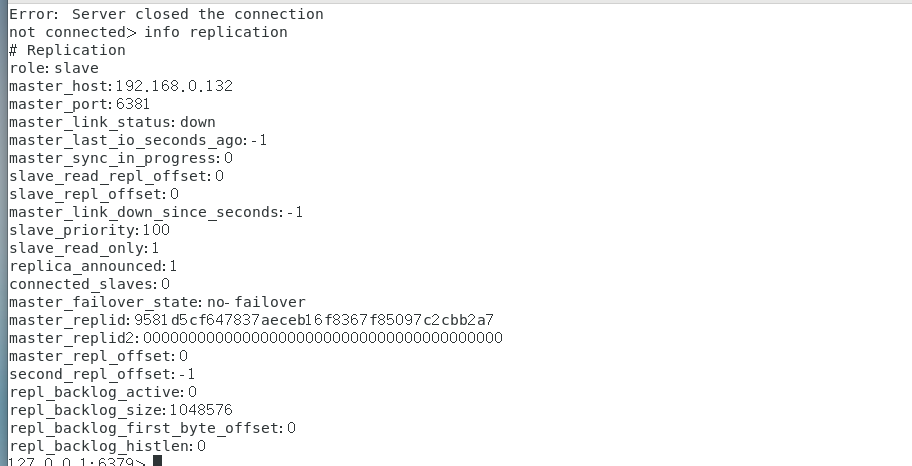
可以看到可以正常访问数据
结论
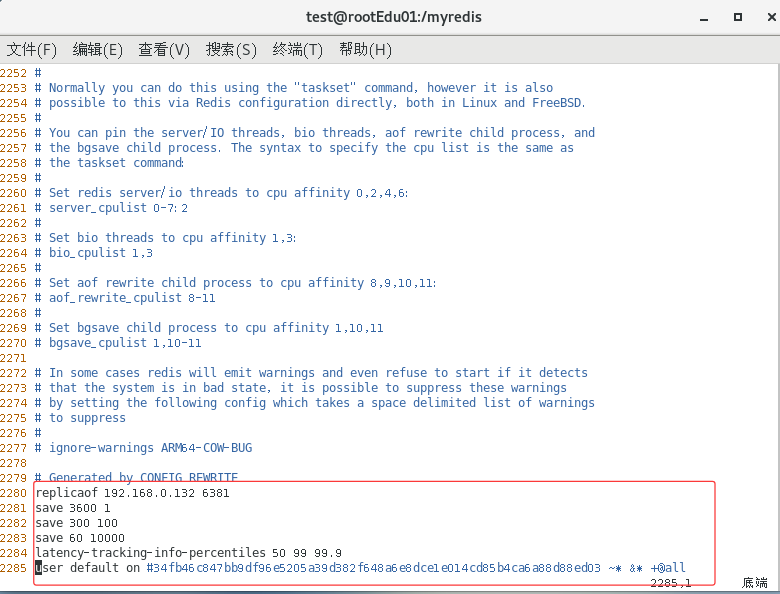
- 文件的内容,在运行期间会被自动sentinel动态进行更改
- master-slave 切换后,master_redis.conf、slave_redis.conf和sentinel.conf的内容都会发生改变,即master_redis.conf 中会多一行slaveof的配置,sentinel.conf 的监控目标会随之调换
运行流程和选举原理
当一个主从配置中的master失效之后,sentinel可以选举出一个新的master用于自动接替原master的工作,主从配置中的其他redis服务器自动指向新的master同步数据。一般建议sentinel采取奇数台,防止某一台sentinel无法连接到master导致误切换
运行流程,故障切换
三个哨兵监控一主二从,正常运行中
SDown主观下线(Subjectively Down):
SDown(主观不可用)是单个sentinel自己主观上检测到的关于master的状态,从sentinel的角度来看,如果发送了PING心跳后,在一定时间内没有收到合法的回复,就达到 SDOWN 的条件
sentinel 配置文件中的 down-after-milisenconds 设置了判断主观下线的时间长度
说明:
所谓主观下线(Subjectively Down, 简称 SDOWN)指的是单个Sentinel实例对服务器做出的下线判断,即单个sentinel认为某个服务下线(有可能是接收不到订阅,之间的网络不通等等原因)。主观下线就是说如果服务器在[sentinel down-after-milliseconds]给定的毫秒数之内没有回应PING命令或者返回一个错误消息, 那么这个Sentinel会主观的(单方面的)认为这个master不可以用了,o(╥﹏╥)o

sentinel down-after-milliseconds <masterName> <timeout>
表示master被当前sentinel实例认定为失效的间隔时间,这个配置其实就是进行主观下线的一个依据
master在多长时间内一直没有给Sentine返回有效信息,则认定该master主观下线。也就是说如果多久没联系上redis-servevr,认为这个redis-server进入到失效(SDOWN)状态。
ODown客观下线(Objectively Down)
ODOWN 需要一定数量的 sentinel,多个哨兵达成一致意见才能认为一个master客观上已经宕掉
说明:
四个参数含义:
masterName是对某个master+slave组合的一个区分标识(一套sentinel可以监听多组master+slave这样的组合)
quorum这个参数是进行客观下线的一个依据,法定人数/法定票数
意思是至少有quorum个sentinel认为这个master有故障才会对这个master进行下线以及故障转移。因为有的时候,某个sentinel节点可能因为自身网络原因导致无法连接master,而此时master并没有出现故障,所以这就需要多个sentinel都一致认为该master有问题,才可以进行下一步操作,这就保证了公平性和高可用。
选举出领导者哨兵(哨兵中选出兵王(leader))
当主节点被判断客观下线以后,各个哨兵节点会进行协商,先选举出一个**领导者哨兵节点(兵王)**并由该领导者节点,也即被选举出的兵王进行failover(故障迁移)
哨兵领导者,兵王如何选举出来的?
Raft算法
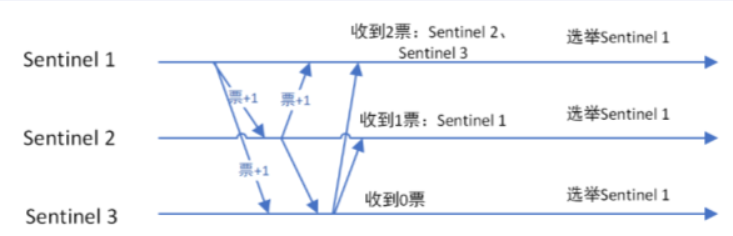
监视该主节点的所有哨兵都有可能被选为领导者,选举使用的算法是Raft算法;Raft算法的基本思路是先到先得:
即在一轮选举中,哨兵A向B发送成为领导者的申请,如果B没有同意过其他哨兵,则会同意A成为领导者
由兵王(leader)开始推动故障切换流程并选出一个新的master
3个步骤
选出新的主节点
某个slave被选中成为新的master
选出新的master的规则,剩余slave节点健康前提下
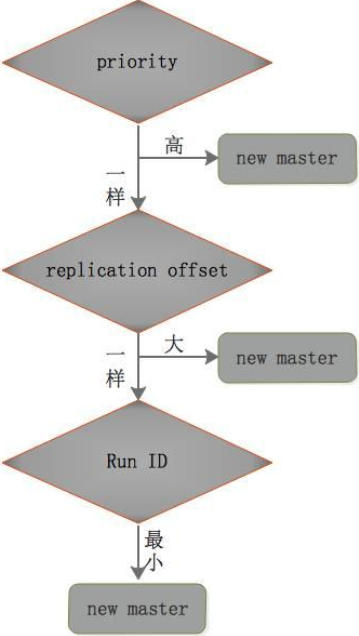
redis.conf文件中,优先级slave-priority或者 replica-priority 最高的从节点(数字越小优先级越高)
复制偏移位置offset最大的从节点
最小Run ID 的从节点
字典顺序,ASCII 码
从机加入到主机上
- 执行slaveof no one 命令让选出来的从节点成为新的主节点,并通过slaveof命令让其他节点成为从节点
- sentinel leader 会对选举出的新master执行slaveof no one操作,将其提升为master节点
- sentinel leader 向其他slave 发送命令,让剩余的slave成为新的master节点的slave
主机up上线会挂在已经上位的主机上
- 将之前已下线的老master设置为新选出的新master的从节点,当老master重新上线后,它会成为新的master的从节点
- sentinel leader 会让原来的master降级为slave并恢复正常工作。
总结
上述的failover操作均由sentinel自己独自完成,无效人工干预。
使用建议
哨兵节点的数量为多个,哨兵本身应该集群,保证高可用
哨兵节点的数量应该是奇数
如果哨兵节点部署在 Docker 等容器里面,尤其要注意端口的正确映射
哨兵集群+主从复制,并不保证数据零丢失
承上启下引出集群
集群(cluster)
由于数据量过大,单个Master复制集难以承担,因此需要对多个复制集进行集群,形成水平扩展每个复制集只负责存储整个数据集的一部分,这就是Redis的集群,其作用是提供在多个Redis节点间共享数据的程序集。

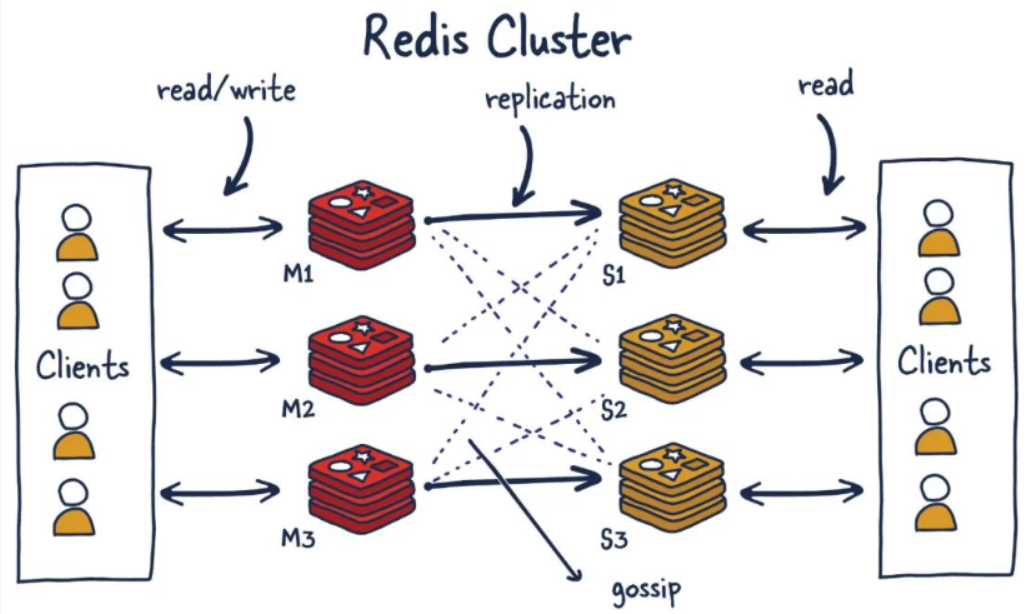
redis 集群是一个提供在多个redis节点间共享数据的程序集
redis集群可以支持多个master
能干嘛?
- redis 集群支持多个 master,每个master又可以挂在多个 slave
- 读写分离
- 支持数据的高可用
- 支持海量数据的读写存储操作
- 由于 cluster 自带 sentinel 的故障转移机制,内置了高可用的支持,无需再去使用哨兵功能
- 客户端与redis的节点连接,不再需要连接集群中所有的节点,只需要任意连接集群中的一个可用节点即可
- 槽位slot负责分配到各个物理服务节点,由对应的集群来负责维护节点、插槽和数据之间的关系
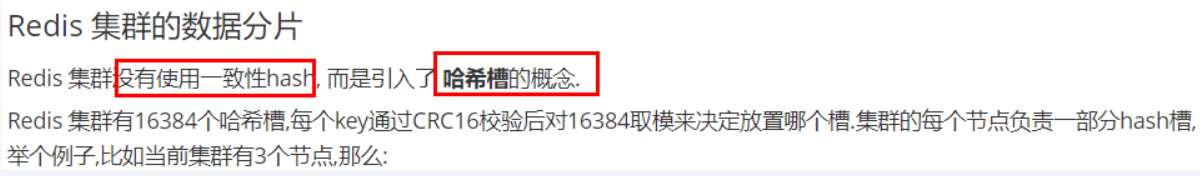
集群算法-分片-槽位slot
集群的秘钥空间被分成 16384个槽,有效地设置了 16384 个主节点的集群大小限(但是,建议的最大节点大小约1000个节点)。
集群中的每个主节点处理16384个哈希槽的一个子集。当没有集群重新配置正在进行时(即哈希槽从一个节点移动到另一个节点),集群是稳定的。当集群稳定时,单个哈希槽将由单个节点提供服务(但是,服务节点可以有一个或多个副本),在网络分裂或故障的情况下替换它,并且可以用于扩展 读取陈旧数据是可接受的操作。
redis集群的槽位slot
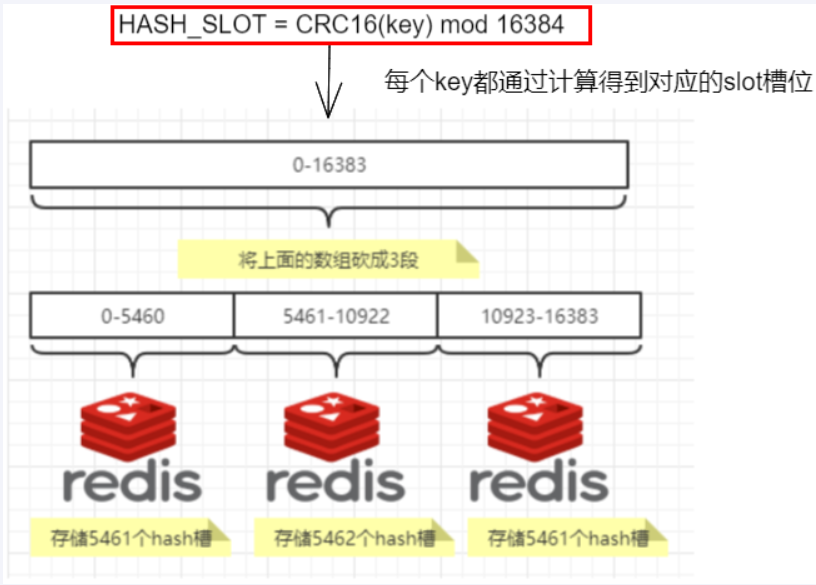
redis集群的分片
分片是什么?
使用Redis集群时我们会将存储的数据分散到多台redis机器上,这称为分片。简言之,集群中的每个Redis实例都被认为是整个数据的一个分片。
如何找到给定key的分片?
为了找到给定key的分片,我们对key进行CRC16(key)算法处理并通过对总分片数量取模。然后,使用确定性哈希函数,这意味着给定的key将多次始终映射到同一个分片,我们可以推断将来读取特定key的位置。
redis集群的槽位和分片的优势
最大优势,方便扩缩容和数据分派查找
这种结构很容易添加或者删除节点,比如如果我想添加个节点D,我需要从节点 A,B,C中得到部分槽到 D上 。如果我想移除节点A,需要将 A 中的槽移到B和C节点上,然后将没有任何槽的A节点从集群中移除即可。由于从一个节点将哈希槽移动到另一个节点并不会停止服务,所以无论添加删除或者改变某个节点的哈希槽的数量都不会造成集群不可用的状态。
slot槽位映射,一般业界有3种解决方案
哈希取余分区
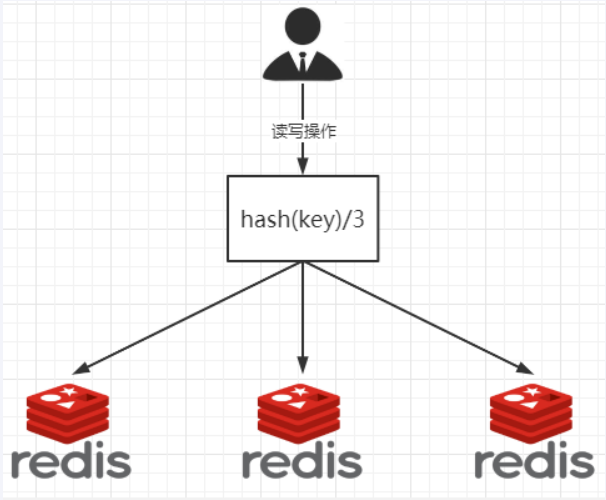
2亿条记录就是2亿个k,v,我们单机不行必须要分布式多机,假设有3台机器构成一个集群,用户每次读写操作都是根据公式:hash(key) % N个机器台数,计算出哈希值,用来决定数据映射到哪一个节点上。
优点:
简单粗暴,直接有效,只需要预估好数据规划好节点,例如3台、8台、10台,就能保证一段时间的数据支撑。使用Hash算法让固定的一部分请求落到同一台服务器上,这样每台服务器固定处理一部分请求(并维护这些请求的信息),起到负载均衡+分而治之的作用。
缺点:
原来规划好的节点,进行扩容或者缩容就比较麻烦了额,不管扩缩,每次数据变动导致节点有变动,映射关系需要重新进行计算,在服务器个数固定不变时没有问题,如果需要弹性扩容或故障停机的情况下,原来的取模公式就会发生变化:Hash(key)/3会变成Hash(key) /?。此时地址经过取余运算的结果将发生很大变化,根据公式获取的服务器也会变得不可控。
某个redis机器宕机了,由于台数数量变化,会导致hash取余全部数据重新洗牌。
一致性哈希算法分区
一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院中提出的,设计目标是为了解决分布式缓存数据变动和映射问题,某个机器宕机了,分母数量改变了,自然取余数不OK了。
能干嘛?
提出一致性Hash 解决方案。目的是当服务器个数发生变动时,尽量减少影响客户端到服务器的映射关系
三大步骤
算法构建一致性哈希环
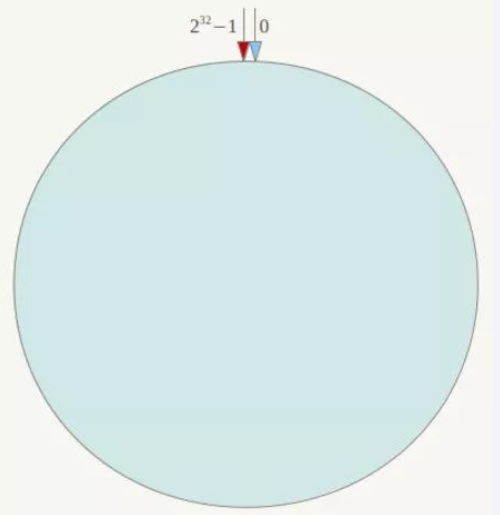
一致性哈希算法必然有个hash函数并按照算法产生hash值,这个算法的所有可能哈希值会构成一个全量集,这个集合可以成为一个hash空间[0,2^32-1],这个是一个线性空间,但是在算法中,我们通过适当的逻辑控制将它首尾相连(0 = 2^32),这样让它逻辑上形成了一个环形空间。
它也是按照使用取模的方法,前面笔记介绍的节点取模法是对节点(服务器)的数量进行取模。而一致性Hash算法是对2^32取模,简单来说,一致性Hash算法将整个哈希值空间组织成一个虚拟的圆环,如假设某哈希函数H的值空间为0-2^32-1(即哈希值是一个32位无符号整形),整个哈希环如下图:整个空间按顺时针方向组织,圆环的正上方的点代表0,0点右侧的第一个点代表1,以此类推,2、3、4、……直到2^32-1,也就是说0点左侧的第一个点代表2^32-1, 0和2^32-1在零点中方向重合,我们把这个由2^32个点组成的圆环称为Hash环。
redis服务器IP节点映射
将集群中各个IP节点映射到环上的某一个位置。
将各个服务器使用Hash进行一个哈希,具体可以选择服务器的IP或主机名作为关键字进行哈希,这样每台机器就能确定其在哈希环上的位置。假如4个节点NodeA、B、C、D,经过IP地址的哈希函数计算(hash(ip)),使用IP地址哈希后在环空间的位置如下:
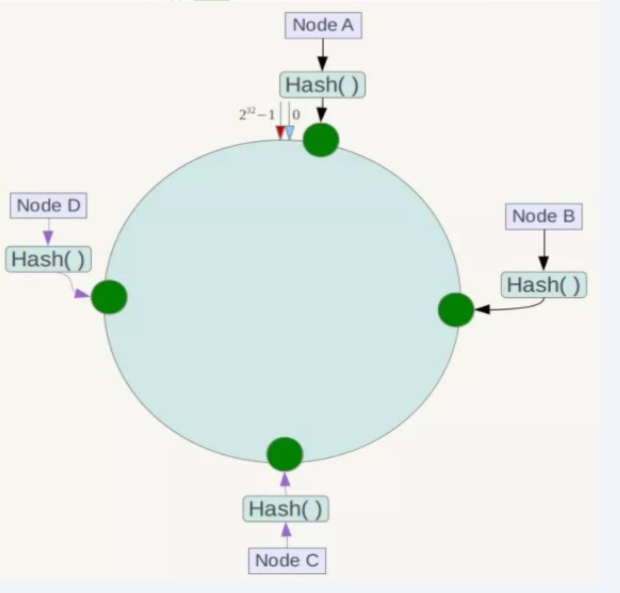
key落到服务器的落键规则
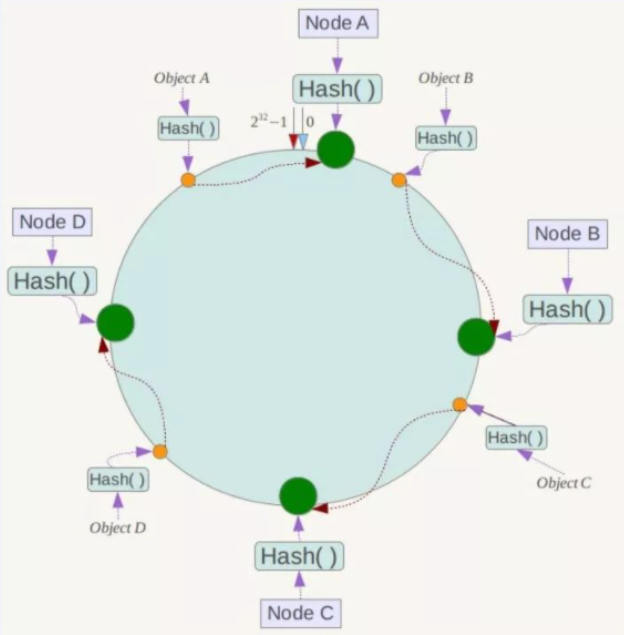
当我们需要存储一个kv键值对时,首先计算key的hash值,hash(key),将这个key使用相同的函数Hash计算出哈希值并确定此数据在环上的位置,从此位置沿环顺时针“行走”,第一台遇到的服务器就是其应该定位到的服务器,并将该键值对存储在该节点上。
如我们有Object A、Object B、Object C、Object D四个数据对象,经过哈希计算后,在环空间上的位置如下:根据一致性Hash算法,数据A会被定为到Node A上,B被定为到Node B上,C被定为到Node C上,D被定为到Node D上。
优点
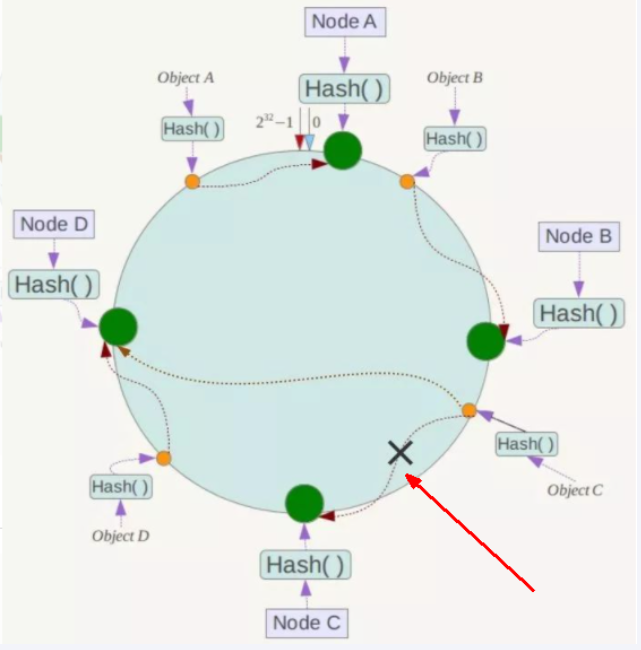
一致性哈希算法的容错性
假设Node C宕机,可以看到此时对象A、B、D不会受到影响。一般的,在一致性Hash算法中,如果一台服务器不可用,则受影响的数据仅仅是此服务器到其环空间中前一台服务器(即沿着逆时针方向行走遇到的第一台服务器)之间数据,其它不会受到影响。简单说,就是C挂了,受到影响的只是B、C之间的数据且这些数据会转移到D进行存储。
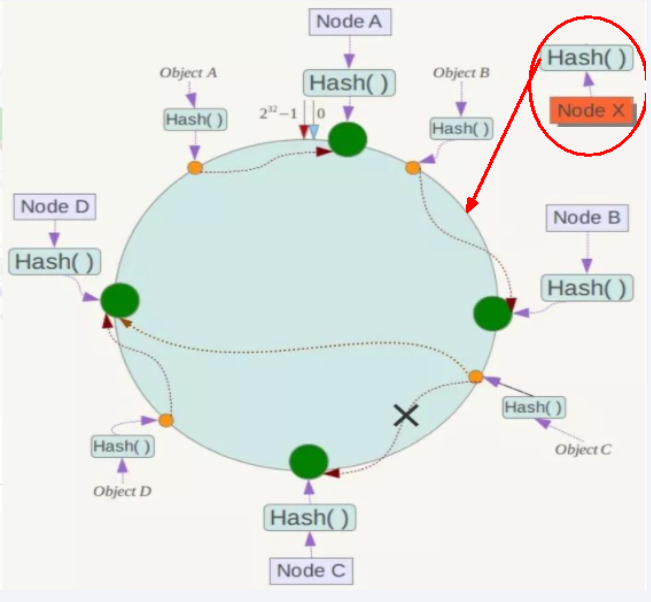
一致性哈希算法的扩展性
数据量增加了,需要增加一台节点NodeX,X的位置在A和B之间,那收到影响的也就是A到X之间的数据,重新把A到X的数据录入到X上即可,
不会导致hash取余全部数据重新洗牌(数据丢失)。
缺点
一致性哈希算法的数据倾斜问题
一致性Hash算法在服务节点太少时,容易因为节点分布不均匀而造成数据倾斜(被缓存的对象大部分集中缓存在某一台服务器上)问题,
例如系统中只有两台服务器:
总结
为了在节点数目发生改变时尽可能少的迁移数据
将所有的存储节点排列在收尾相接的Hash环上,每个key在计算Hash后会顺时针找到临近的存储节点存放。
而当有节点加入或退出时仅影响该节点在Hash环上顺时针相邻的后续节点。
优点:
加入和删除节点只影响哈希环中顺时针方向的相邻的节点,对其他节点无影响。
缺点:
数据的分布和节点的位置有关,因为这些节点不是均匀的分布在哈希环上的,所以数据在进行存储时达不到均匀分布的效果。
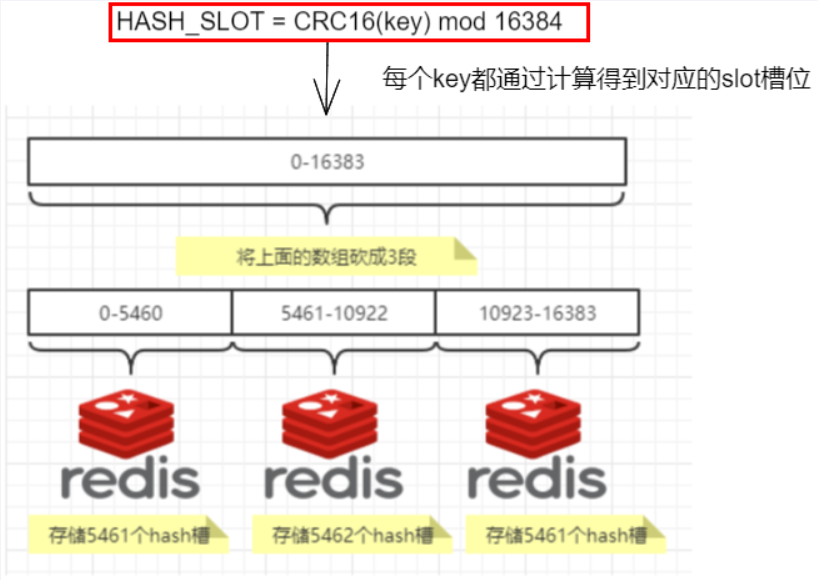
哈希槽分区(HASH_SLOT=CRC16(key) mod 16384)
为什么会出现?
一致性哈希算法的数据倾斜问题
哈希槽实质就是一个数组,数组[0,2^14 -1]形成hash slot空间。
能干什么
解决均匀分配的问题,在数据和节点之间又加入了一层,把这层称为哈希槽(slot),用于管理数据和节点之间的关系,现在就相当于节点上放的是槽,槽里放的是数据。
槽解决的是粒度问题,相当于把粒度变大了,这样便于数据移动。哈希解决的是映射问题,使用key的哈希值来计算所在的槽,便于数据分配
多少个hash槽
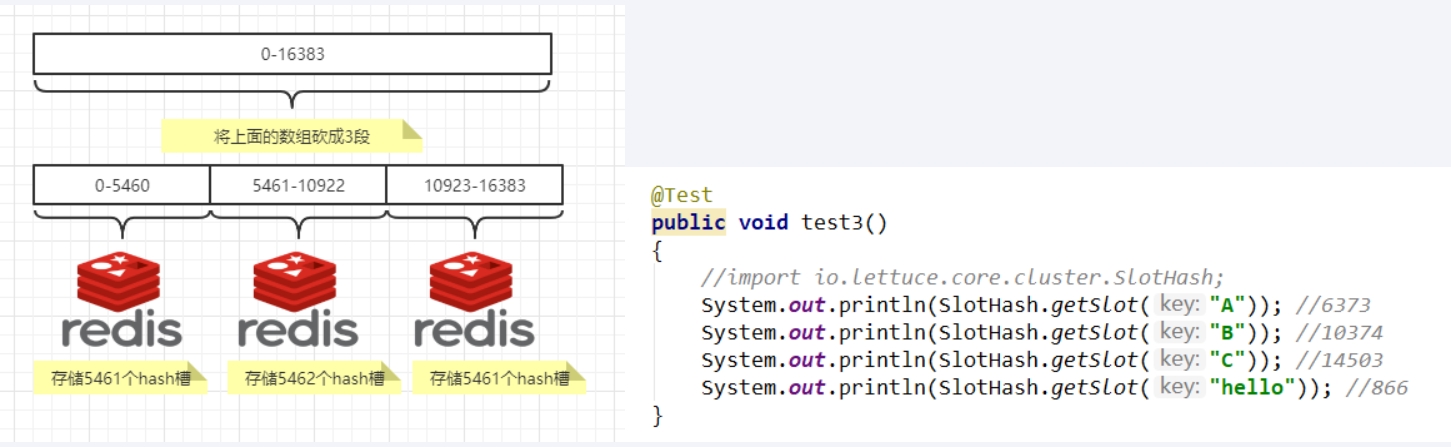
一个集群只能有16384个槽,编号0-16383(0-2^14-1)。这些槽会分配给集群中的所有主节点,分配策略没有要求。
集群会记录节点和槽的对应关系,解决了节点和槽的关系后,接下来就需要对key求哈希值,然后对16384取模,余数是几key就落入对应的槽里。HASH_SLOT = CRC16(key) mod 16384。以槽为单位移动数据,因为槽的数目是固定的,处理起来比较容易,这样数据移动问题就解决了。
哈希槽计算
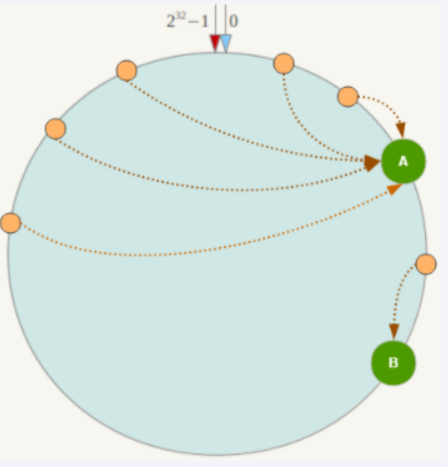
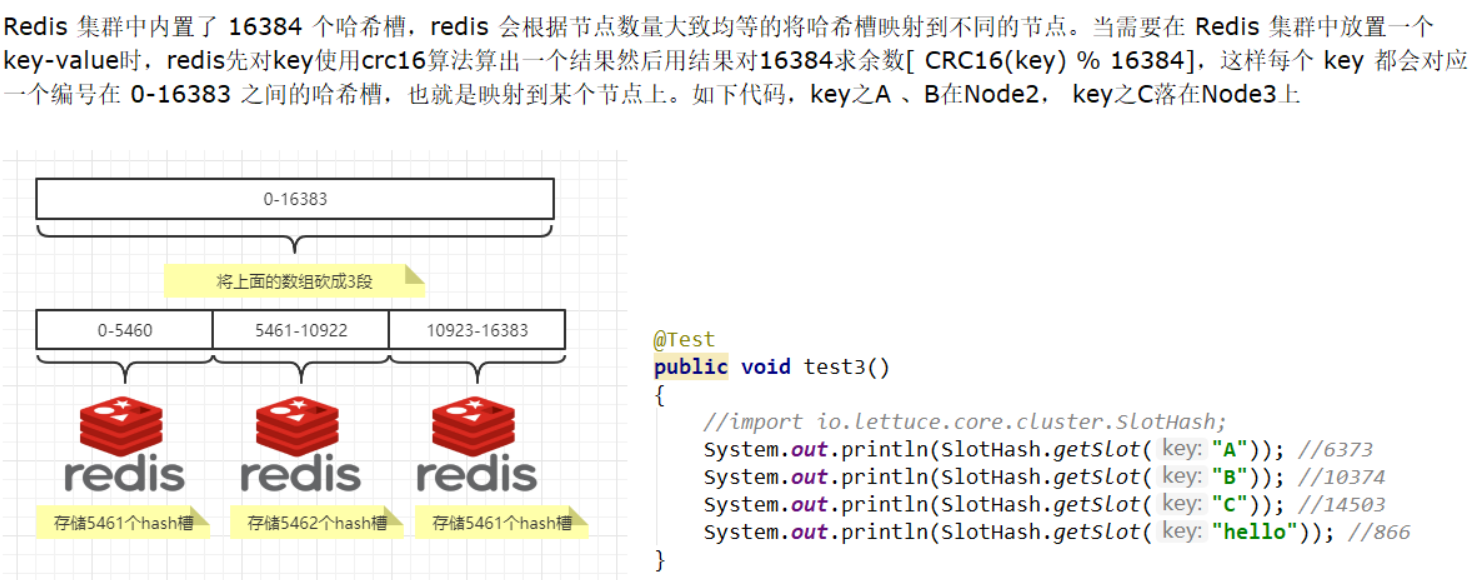
Redis 集群中内置了 16384 个哈希槽,redis 会根据节点数量大致均等的将哈希槽映射到不同的节点。当需要在 Redis 集群中放置一个 key-value时,redis先对key使用crc16算法算出一个结果然后用结果对16384求余数[ CRC16(key) % 16384],这样每个 key 都会对应一个编号在 0-16383 之间的哈希槽,也就是映射到某个节点上。如下代码,key之A 、B在Node2, key之C落在Node3上
为什么redis集群的最大槽数是16384个?
Redis集群并没有使用一致性hash而是引入了哈希槽的概念。Redis 集群有16384个哈希槽,每个key通过CRC16校验后对16384取模来决定放置哪个槽,集群的每个节点负责一部分hash槽。但为什么哈希槽的数量是16384(2^14)个呢?
CRC16算法产生的hash值有16bit,该算法可以产生2^16=65536个值。换句话说值是分布在0~65535之间,有更大的65536不用为什么只用16384就够?作者在做mod运算的时候,为什么不mod65536,而选择mod16384? HASH_SLOT = CRC16(key) mod 65536为什么没启用
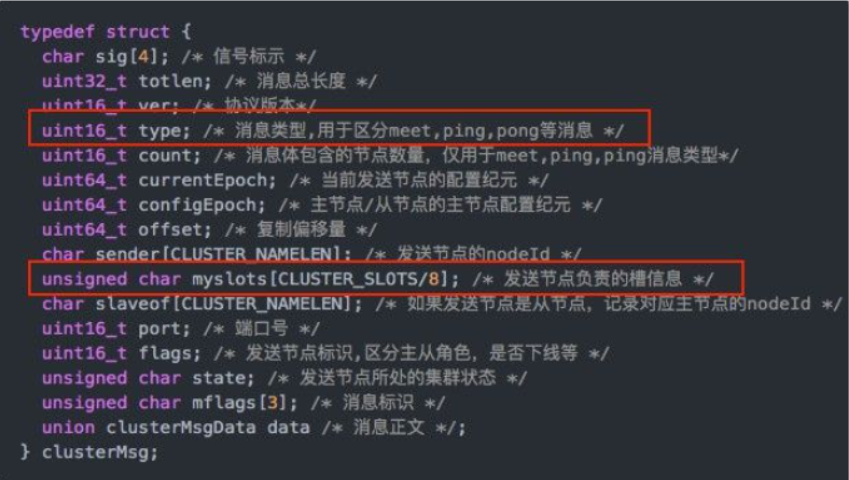
如果槽位为65536,发送心跳信息的消息头达8k,发送的心跳包过于庞大。
在消息头中最占空间的是myslots[CLUSTER_SLOTS/8]。 当槽位为65536时,这块的大小是: 65536÷8÷1024=8kb 在消息头中最占空间的是myslots[CLUSTER_SLOTS/8]。 当槽位为16384时,这块的大小是: 16384÷8÷1024=2kb 因为每秒钟,redis节点需要发送一定数量的ping消息作为心跳包,如果槽位为65536,这个ping消息的消息头太大了,浪费带宽。
redis的集群主节点数量基本不可能超过1000个。
集群节点越多,心跳包的消息体内携带的数据越多。如果节点过1000个,也会导致网络拥堵。因此redis作者不建议redis cluster节点数量超过1000个。 那么,对于节点数在1000以内的redis cluster集群,16384个槽位够用了。没有必要拓展到65536个。
槽位越小,节点少的情况下,压缩比高,容易传输
Redis主节点的配置信息中它所负责的哈希槽是通过一张bitmap的形式来保存的,在传输过程中会对bitmap进行压缩,但是如果bitmap的填充率slots / N很高的话(N表示节点数),bitmap的压缩率就很低。 如果节点数很少,而哈希槽数量很多的话,bitmap的压缩率就很低。
结论
redis集群不保证强一致性,这意味着在特定的条件下,redis集群可能会丢掉一些被系统收到的写入请求命令
3主3从redis集群的配置
找3台真实的虚拟机,各自新建 mkdir -p /myredis/cluster
IP: 192.168.0.128+端口6381/6382
新建 redisCluster6381.conf 和 redisCluster6382.conf
vim /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6381.conf
bind 0.0.0.0
daemonize yes
protected-mode no
port 6381 # 端口
logfile "/myredis/cluster/cluster6381.log"
pidfile /myredis/cluster6381.pid
dir /myredis/cluster
dbfilename dump6381.rdb
appendonly yes
appendfilename "appendonly6381.aof"
requirepass redis # redis密码
masterauth redis # 集群密码
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes-6381.conf
cluster-node-timeout 5000redisCluster6381.conf
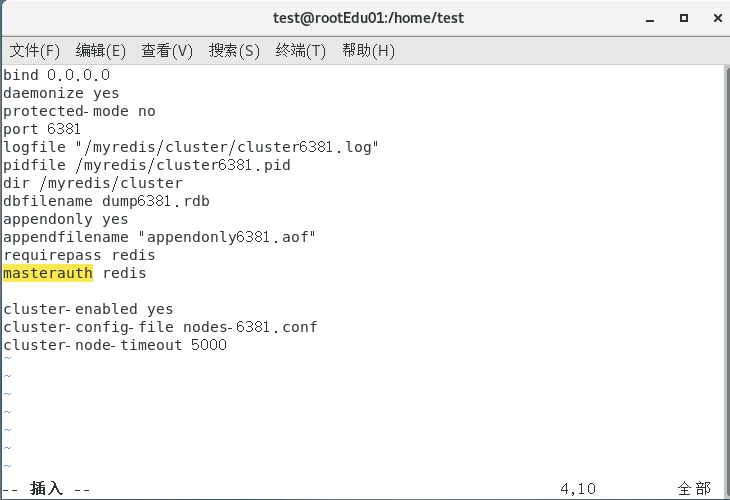
redisCluster6382.conf
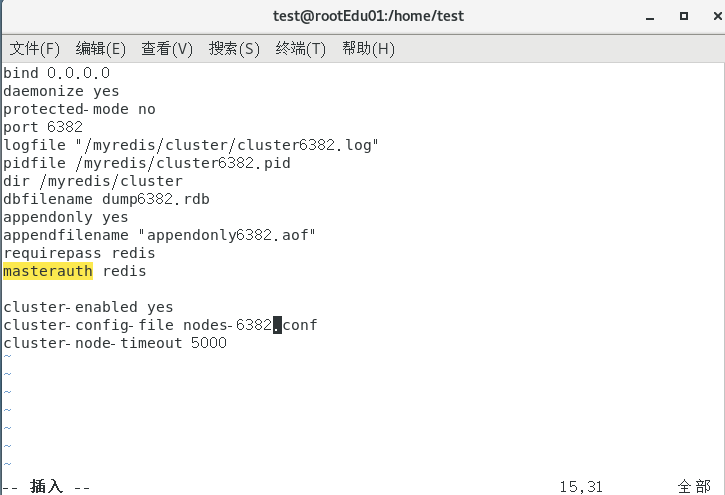
IP: 192.168.0.131+端口6383/6384
新建 redisCluster6383.conf 和 redisCluster6384.conf和 mkdir -p /myredis/cluster文件
vim /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6383.conf和 vim /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6384.conf
redisCluster6383.conf
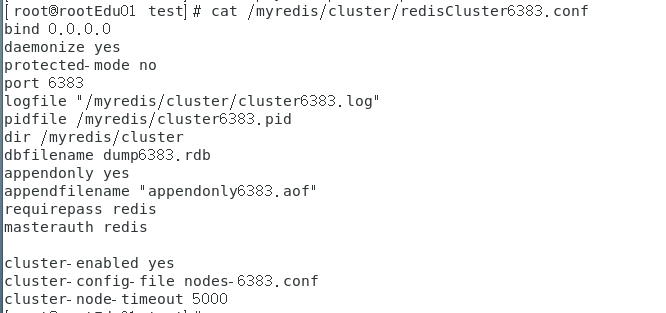
redisCluster6384.conf
IP: 192.168.0.132+端口6385/6386
新建 redisCluster6385.conf 和 redisCluster6386.conf和 mkdir -p /myredis/cluster文件
vim /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6385.conf和 vim /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6386.conf
redisCluster6385.conf
redisCluster6386.conf
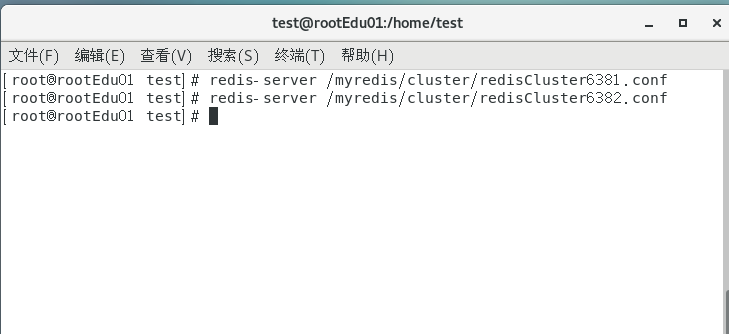
启动redis实例:redis-server /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6381.conf~redis-server /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6386.conf
...
通过redis-cli命令为6台机器构建集群关系
构建主从关系命令
注意,注意,注意自己的真实IP地址
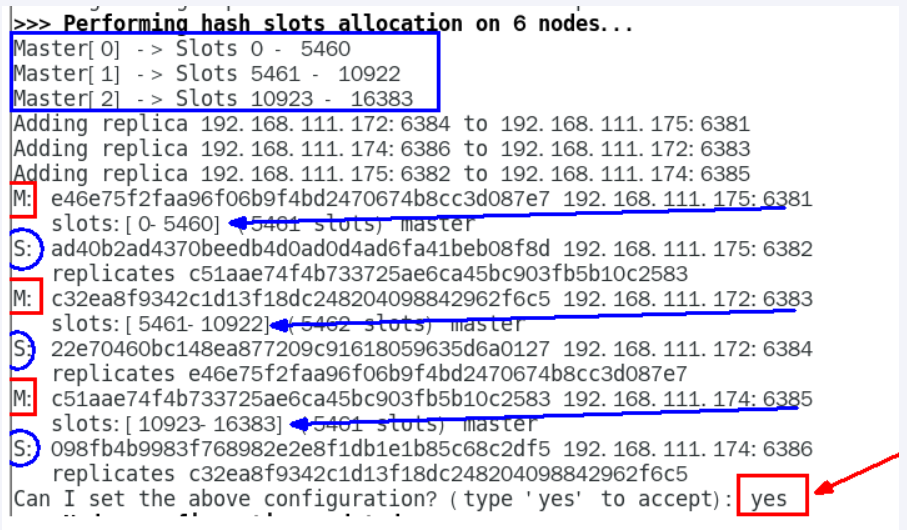
redis-cli -a redis --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 192.168.0.128:6381 192.168.0.128:6382 192.168.0.131:6383 192.168.0.131:6384 192.168.0.132:6385 192.168.0.132:6386
#--cluster-replicas 1 表示为每个master创建一个slave节点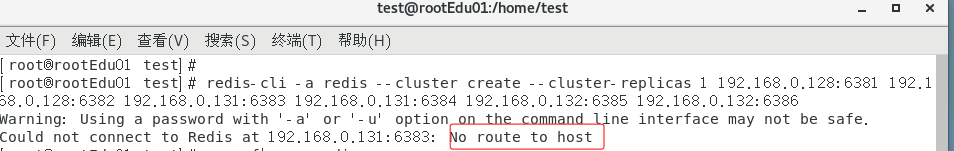
需要关闭3台机器的防火墙,关闭临时防火墙systemctl stop firewalld
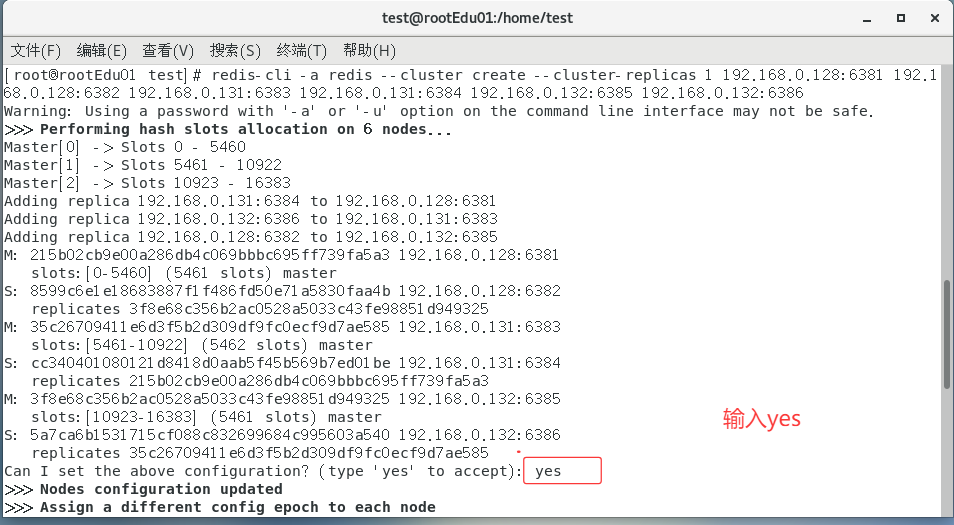
yes问是否3主3从?
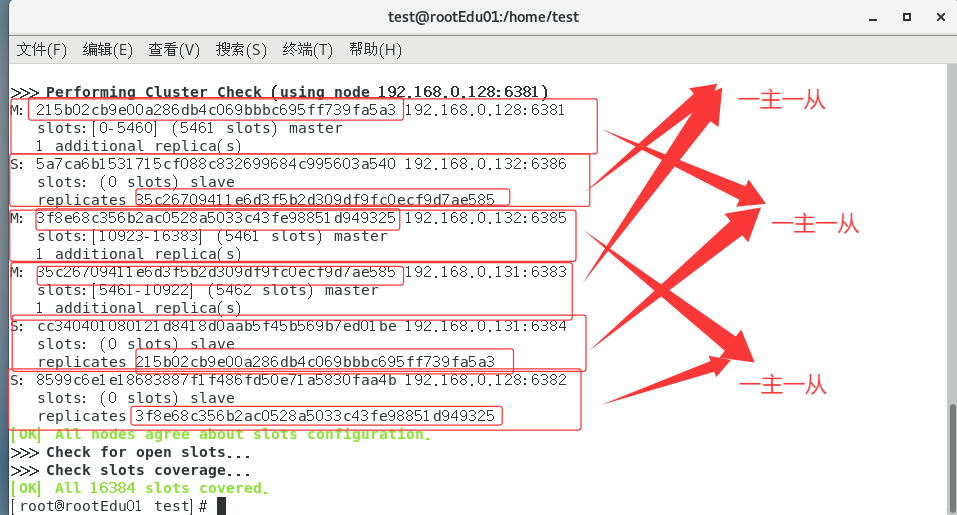
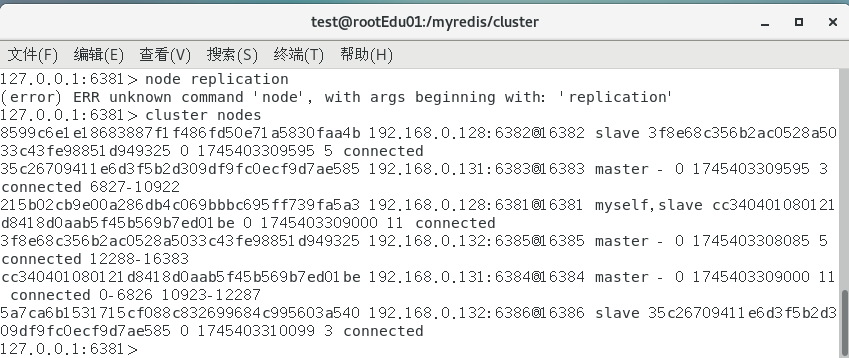
以6381为切入点,查看并检验集群状态
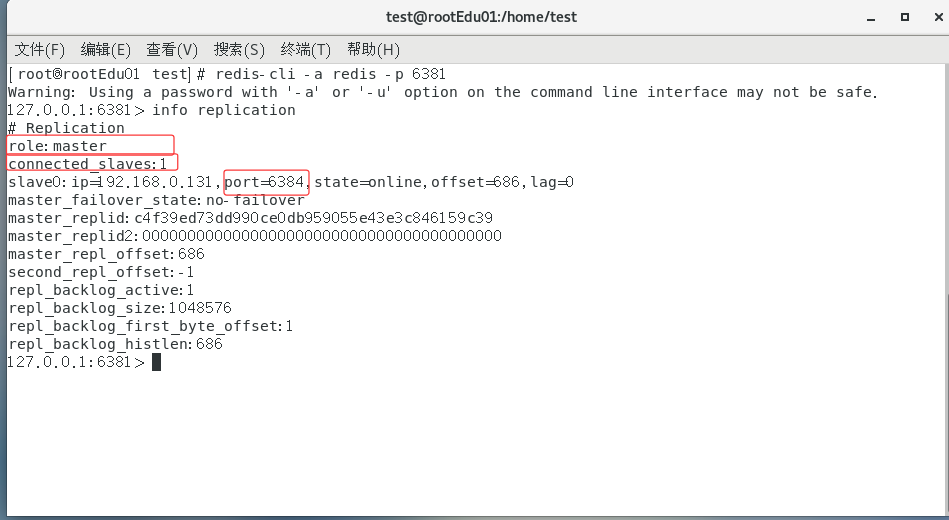
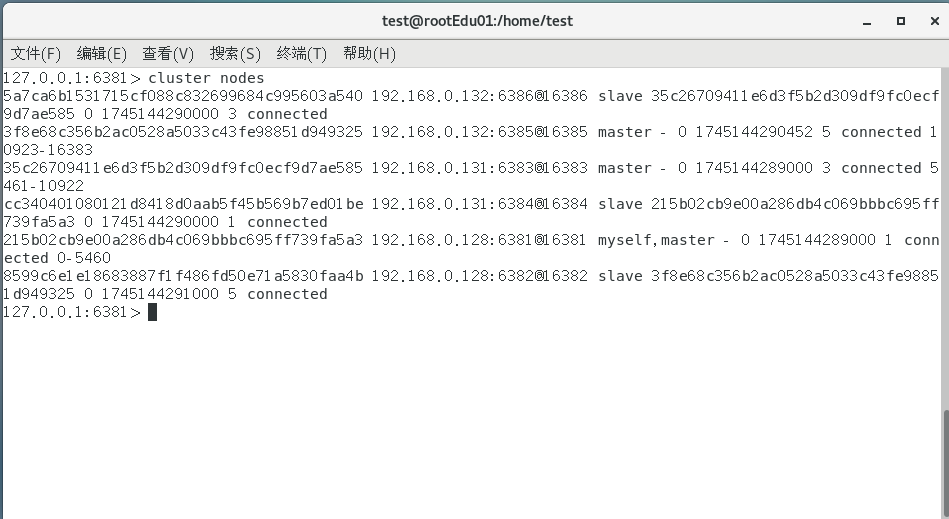
查看节点状态
使用cluster nodes查看
查看单个集群配置cluster info
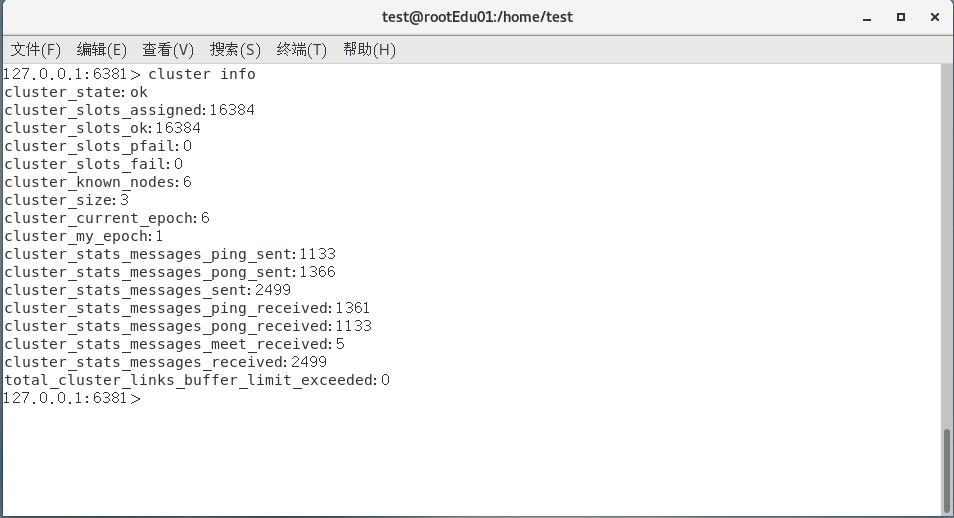
cluster_state:状态是ok节点是否能够接收查询。fail如果至少有一个未绑定的散列槽(没有关联的节点),处于错误状态(为其服务的节点被标记为 FAIL 标记),或者该节点无法到达大多数主节点。cluster_slots_assigned:与某个节点关联的槽数(不是未绑定的)。这个数字应该是16384,节点才能正常工作,这意味着每个散列槽应该映射到一个节点。cluster_slots_ok:映射到不处于FAIL或PFAIL处于状态的节点的散列槽的数量。cluster_slots_pfail:映射到处于PFAIL状态的节点的散列槽的数量。请注意,只要PFAIL状态不由FAIL故障检测算法提升,这些散列槽仍可正常工作。PFAIL仅意味着我们目前无法与节点通话,但可能只是一个暂时的错误。cluster_slots_fail:映射到处于FAIL状态的节点的散列槽的数量。如果此数字不为零,则该节点无法提供查询,除非在配置中cluster-require-full-coverage设置为no。cluster_known_nodes:群集中已知节点的总数,包括HANDSHAKE当前可能不是群集适当成员的状态节点。cluster_size:服务群集中至少一个散列槽的主节点的数量。cluster_current_epoch:局部Current Epoch变量。这用于在故障转移期间创建独特的增加版本号。cluster_my_epoch:我们正在与之交谈的Config Epoch节点。这是分配给此节点的当前配置版本。cluster_stats_messages_sent:通过集群节点到节点二进制总线发送的消息数量。cluster_stats_messages_received:通过集群节点到节点二进制总线接收的消息数量。
3主3从redis集群读写
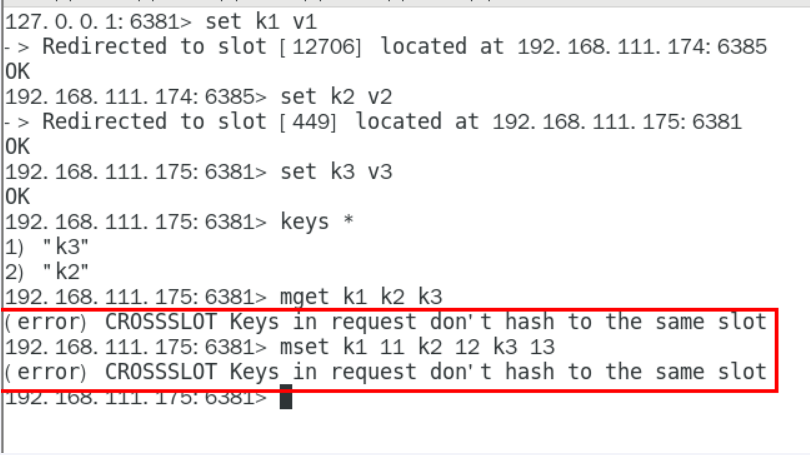
对6381新增两个key,看看效果如何
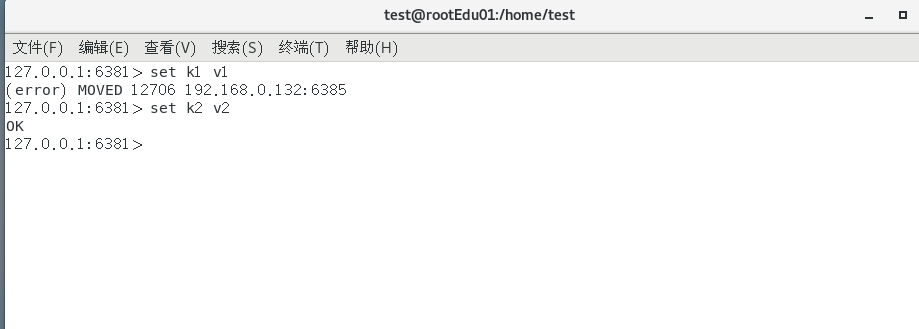
为什么报错
一定注意槽位的范围区间,需要路由到位
如何解决
防止失效加参数-c并新增两个key
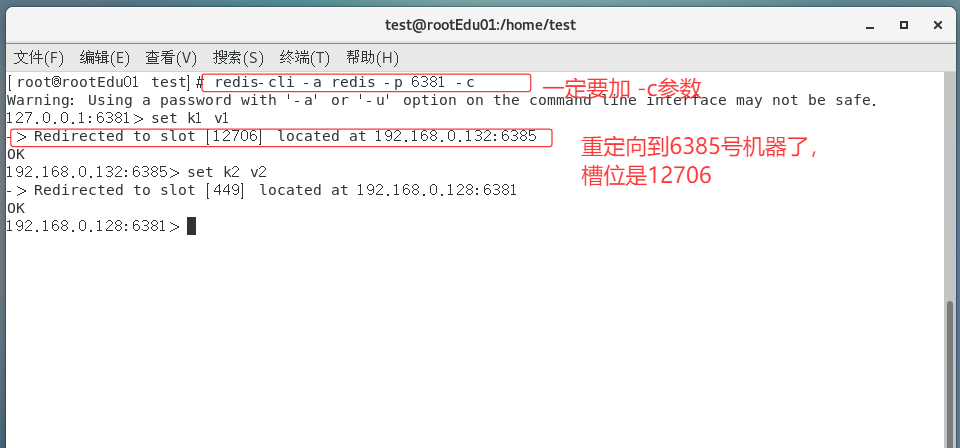
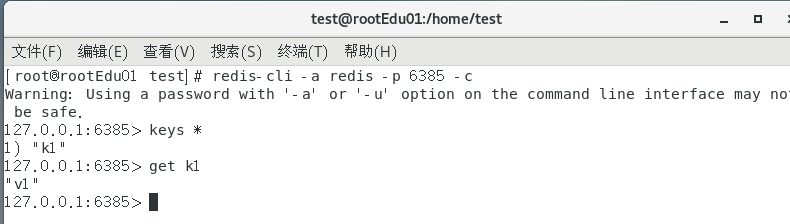
可以看到k1重定向到我们的6385号机器了
如何查看集群信息
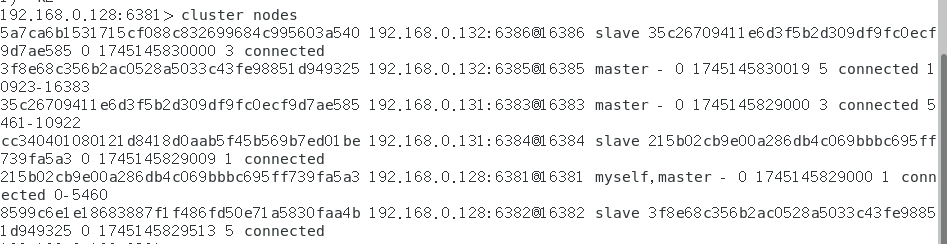
查看某个key该属于对应的槽位值,
cluster keyslot键名称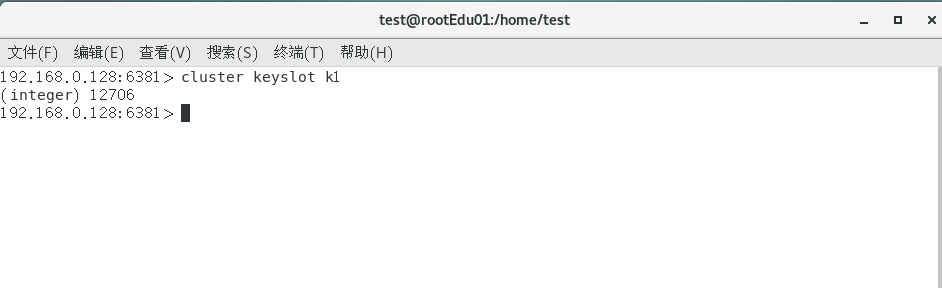
注意:
如果重定向到某一台机器,只能在某一台机器查看,不能在当前机器查看,因为没有数据
主从切换容错切换
容错切换迁移
主6381和从机切换,先停止主机6381
- 6381主机停了,对应的真实从机上位
- 6381作为1号主机分配的从机以实际情况为准,具体几号就是几号(这里是6384)
再次查看集群信息,本次6381主6384从
发现6384,已经成功上位变成主机了!
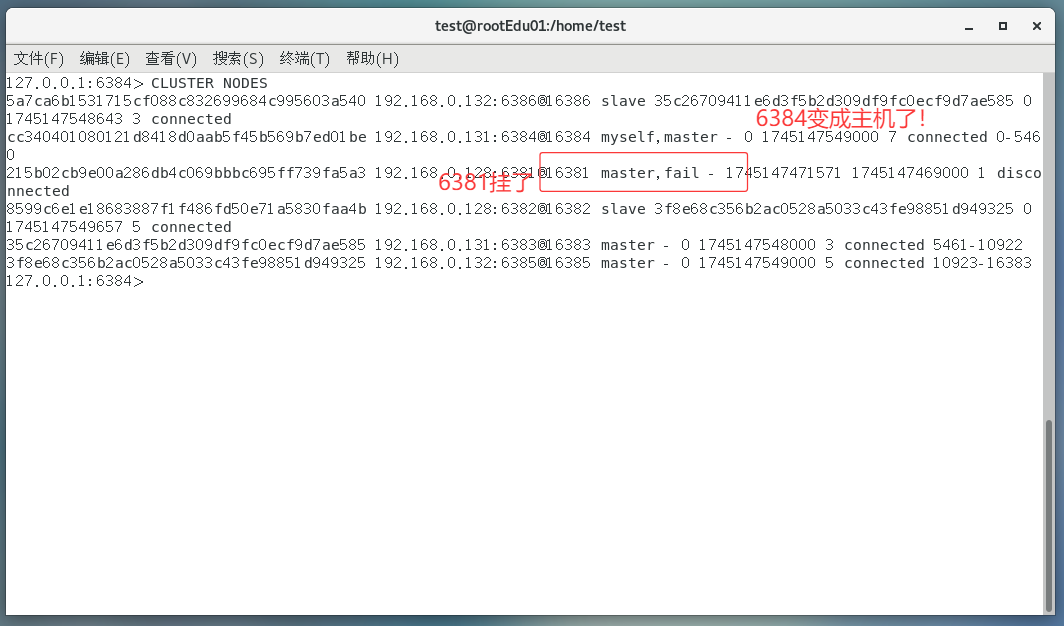
随后,6381原来的主机回来了,是否会上位!
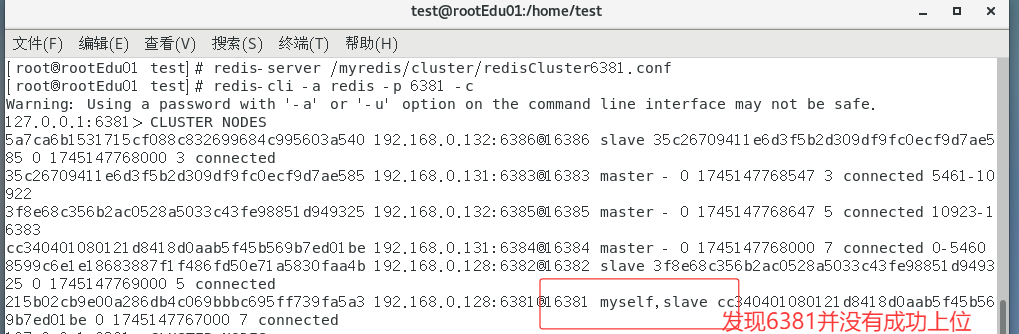
集群不保证数据一致性100%OK,一定会有数据丢失清空
redis集群不保证强一致性,这意味着在特定的条件下,redis集群可能会丢掉一些被系统收到的写入请求命令
手动故障转移 or 节点从属调整该如何处理
使用:
cluster failover可以从从节点变成主节点。当前我们的6381是从节点,我们要把他变成主节点
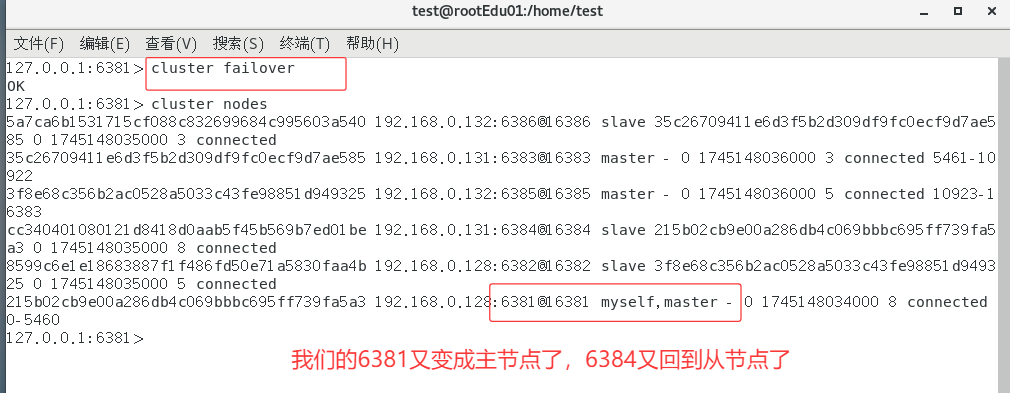
主从扩容案例
当我们的3主3从不够用了,我们就应该扩容
在IP
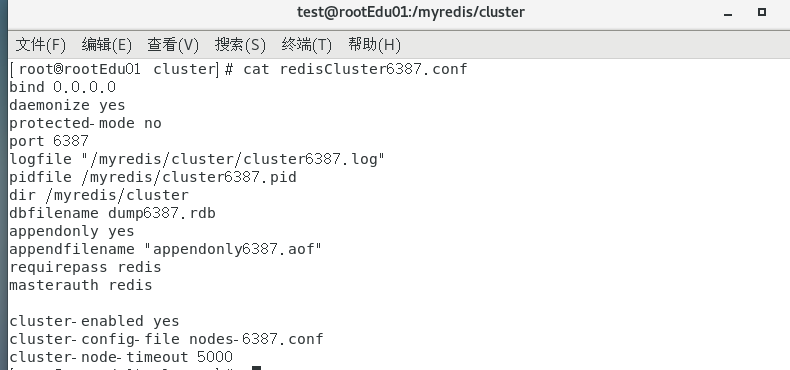
192.168.0.132新建6381、6388两个服务实例配置文件+新建后启动vim /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6387.conf和vim /myredis/cluster/redisCluster6388.conf6387
6388
启动6387和6388
将新增的6387节点(空槽号)作为master节点加入原集群
cmdredis-cli -a 密码 --cluster add-node 自己实际IP地址:6387 自己实际IP地址:6381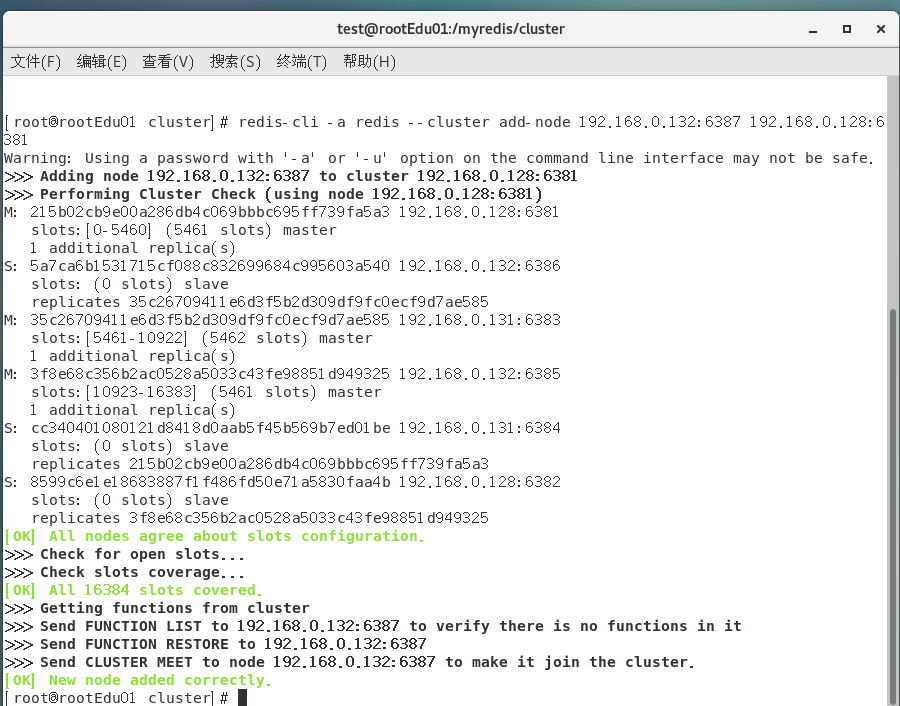
检查集群情况
cmdredis-cli -a 密码 --cluster check 真实ip地址:6381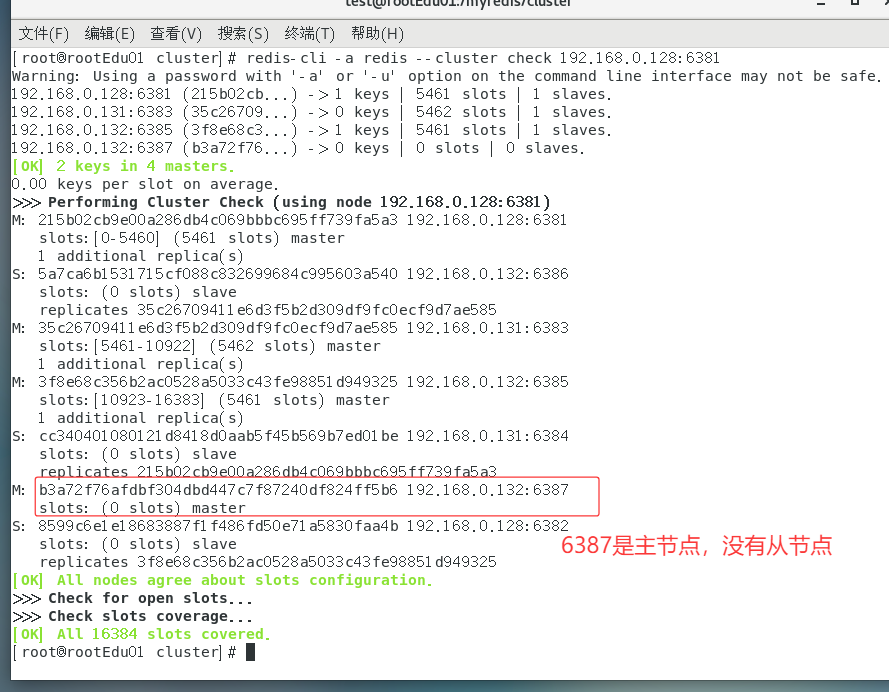
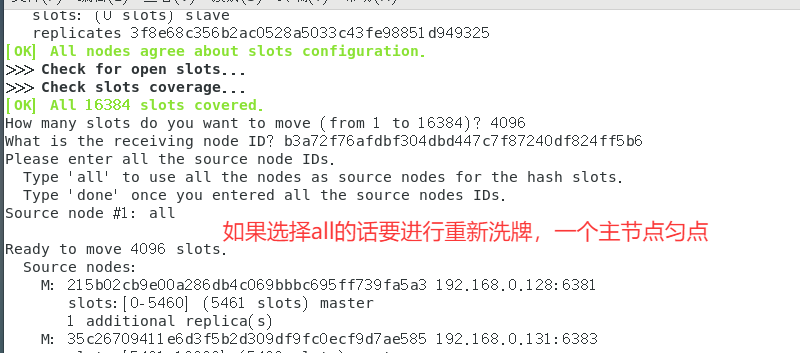
重新分派槽号(reshard)
cmdredis-cli -a 密码 --cluster reshard IP地址:端口号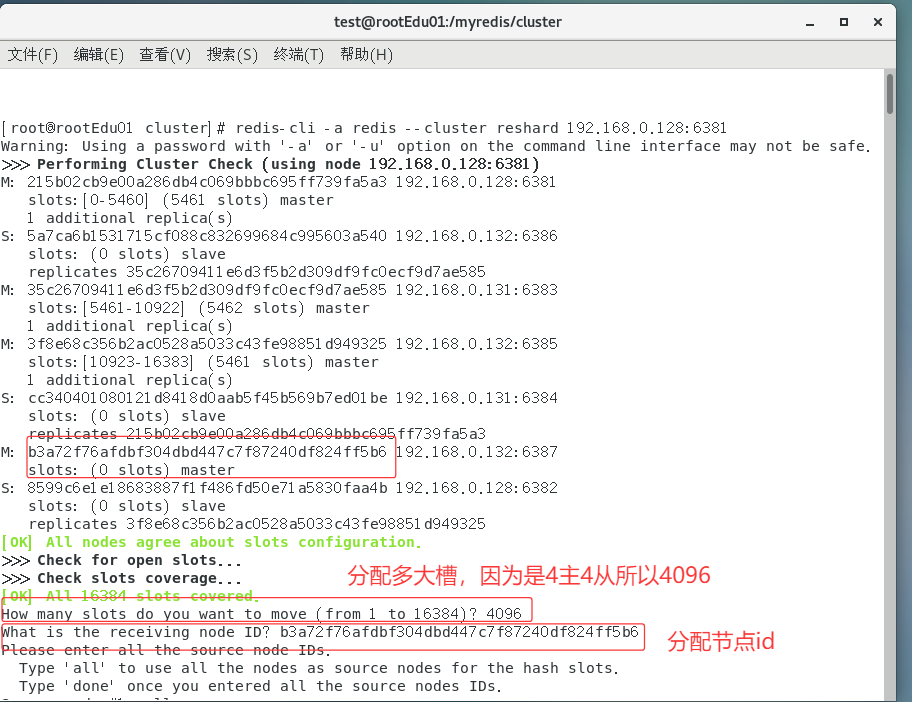
再次检查集群情况
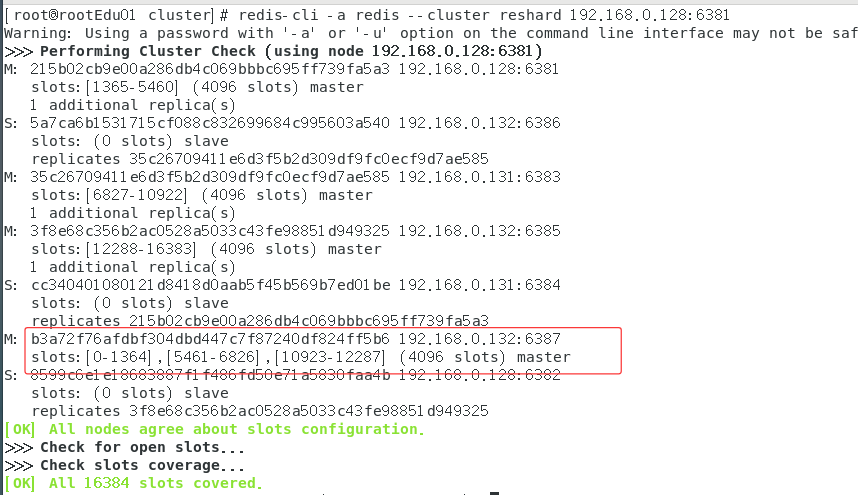
可以看到,在3个主节点上匀了点给第四个主节点了!
为主节点6387分配从节点6388
cmdredis-cli -a 密码 --cluster add-node ip:新slave端口 ip:新master端口 --cluster-slave --cluster-master-id 新主机节点ID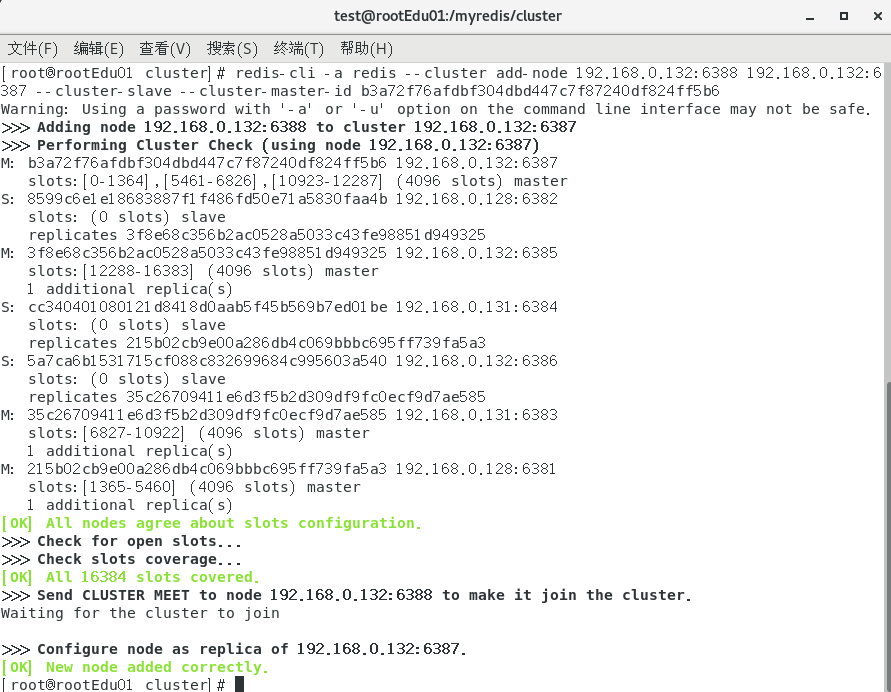
再次检查分配情况
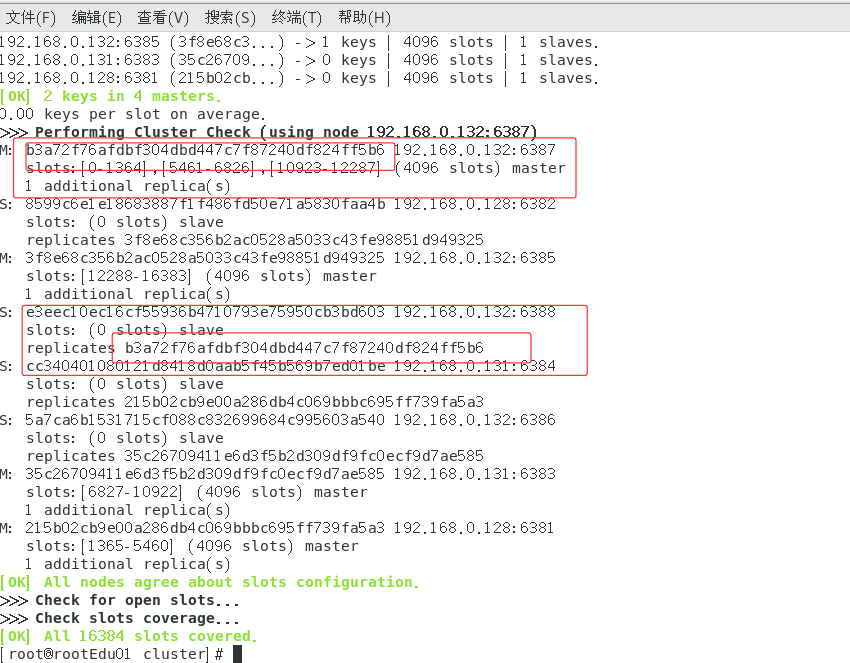
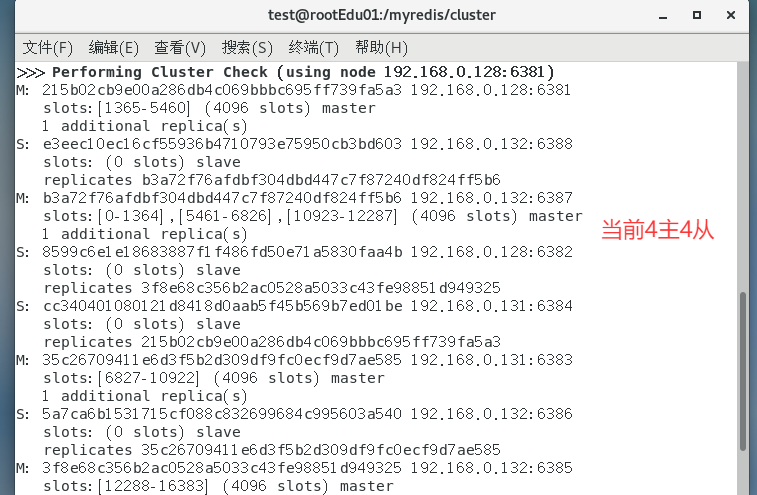
主从缩容案例
目的:让6387和6388下线
从集群中将4号从节点6388删除
redis-cli -a 密码 --cluster del-node ip:从机端口 从机6388节点ID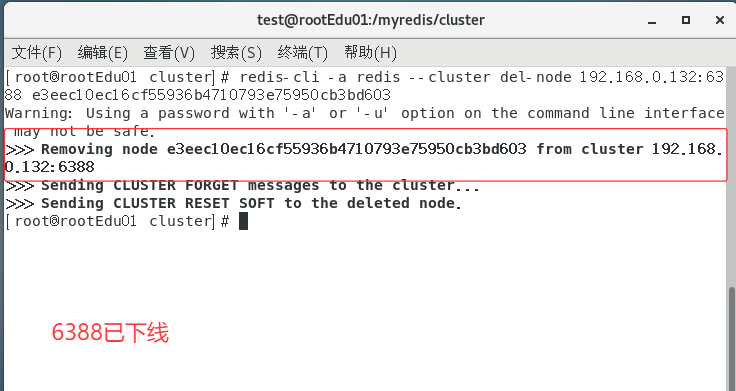
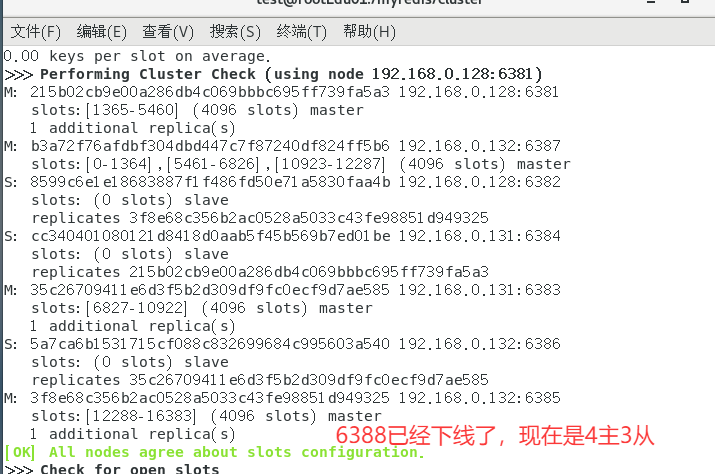
将6387的槽号清空,重新分配,本案例将清出来的槽号都给6381
redis-cli -a redis --cluster reshard 192.168.0.128:6381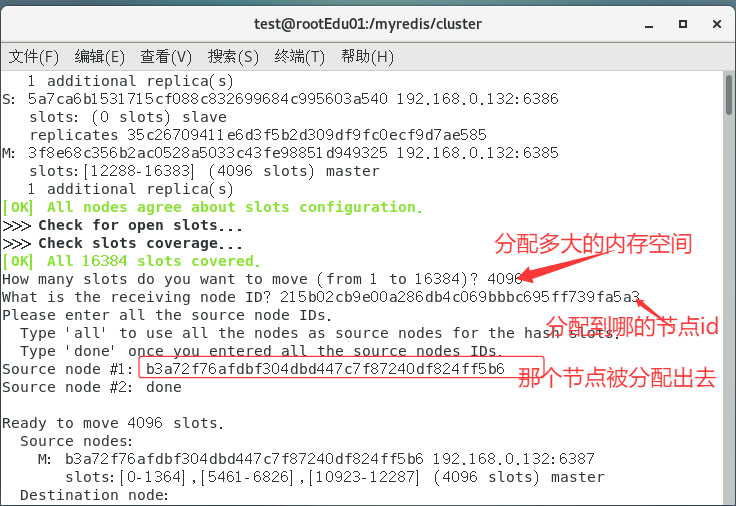
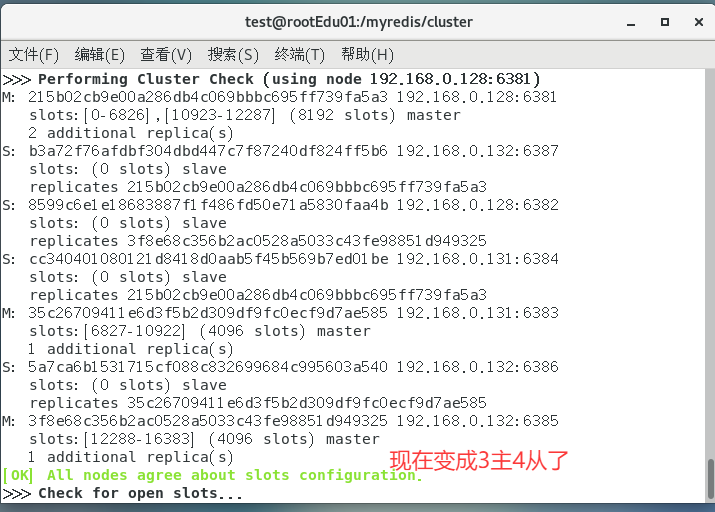
删除6387节点
redis-cli -a 密码 --cluster del-node ip:端口 6387节点ID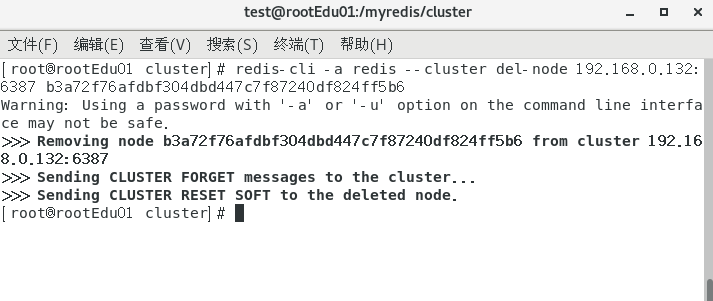
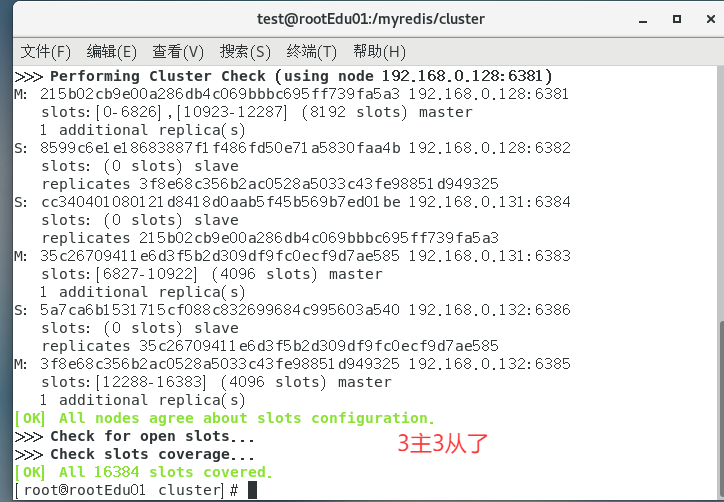
移除成功,再次检查节点
集群常用操作命令和CRC16算法分析
不在同一个slot槽位下的多键操作支持不好,通识占位符登场
不在同一个slot槽位下的键值无法使用mset、mget等多键操作 可以通过{}来定义同一个组的概念,使key中{}内相同内容的键值对放到一个slot槽位去,对照下图类似k1k2k3都映射为x,自然槽位一样 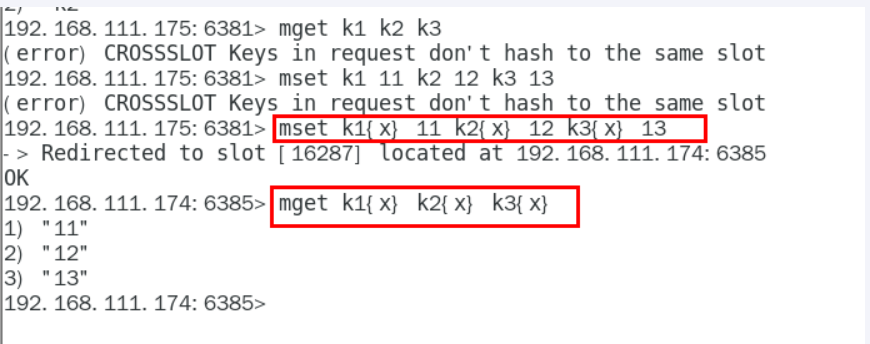
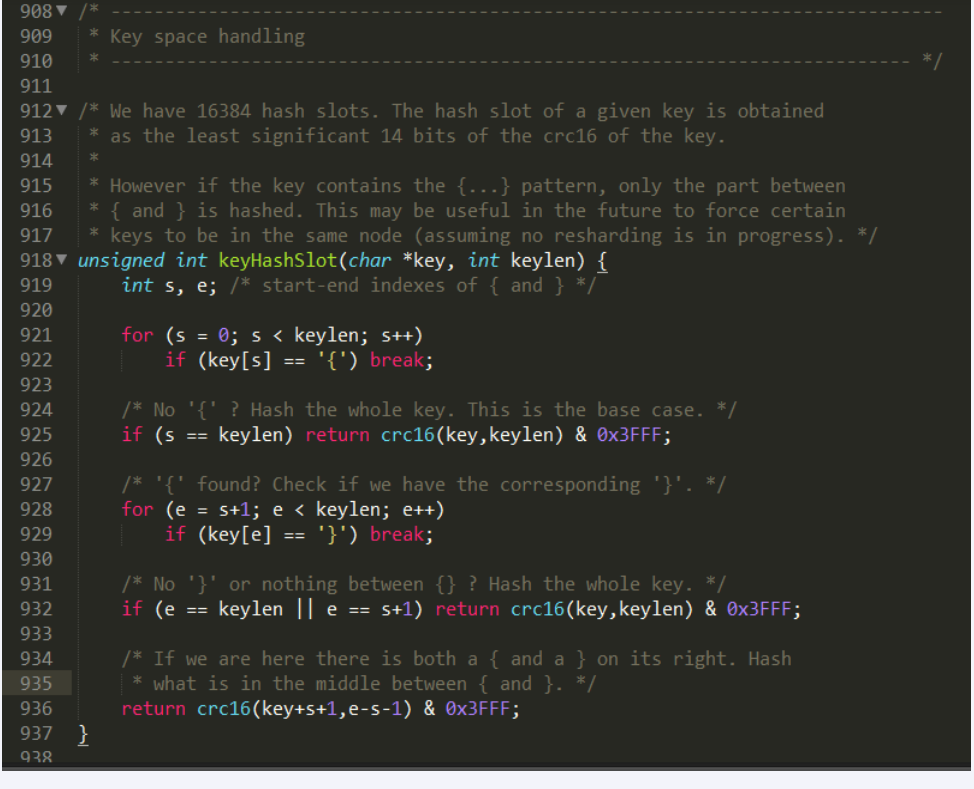
redis集群有16384个哈希槽,每个key通过CRC16校验后对16384取模来决定放置那个槽。集群的每个节点负责一部分hash槽
CRC16源码
cluster.c
常用命令
集群是否完整才能对外提供服务
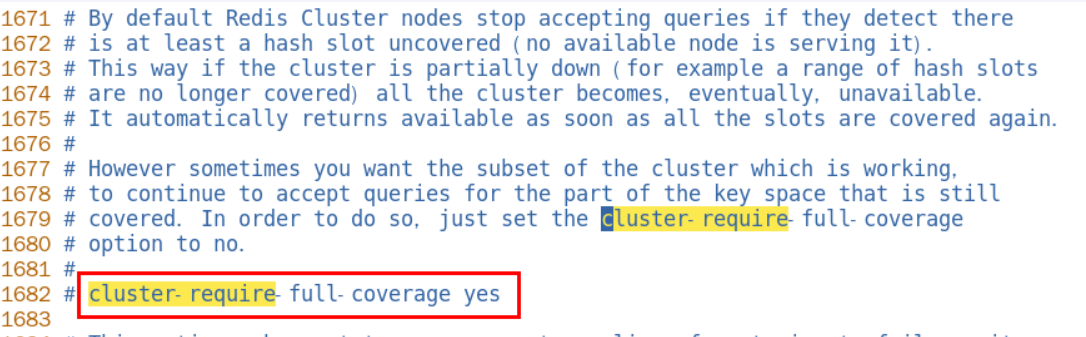
默认YES,现在集群架构是3主3从的redis cluster由3个master平分16384个slot,每个master的小集群负责1/3的slot,对应一部分数据。cluster-require-full-coverage: 默认值 yes , 即需要集群完整性,方可对外提供服务 通常情况,如果这3个小集群中,任何一个(1主1从)挂了,你这个集群对外可提供的数据只有2/3了, 整个集群是不完整的, redis 默认在这种情况下,是不会对外提供服务的。 如果你的诉求是,集群不完整的话也需要对外提供服务,需要将该参数设置为no ,这样的话你挂了的那个小集群是不行了,但是其他的小集群仍然可以对外提供服务。 cluster countkeysinslot槽位数字编号- 1,该槽位被占用
- 0,该槽位没占用
cluster keyslot键名称该键应该存在哪个槽位上
SpringBoot集成Redis
Jedis
Jedis 是一款老牌 Redis 的 Java 客户端。
Jedis Client 是 Redis 官网推荐的一个面向java 客户端,库文件实现了对各类API 进行封装调用
优点:
- Jedis 的 API 提供了比较全面的 Redis 命令的支持
- Jedis 中的 Java 方法基本和 Redis 的 API 保持着一致,也就是说了解 Redis 的API,可以熟练的使用 Jedis
- 支持 pipelining、事务、LUA Scripting、Redis Sentinel、Redis Cluster等等 redis 提供的高级特性
- 客户端轻量,简洁,便于集成和改造
- 使用广泛,开发人员易上手
缺点:
使用阻塞的 I/O 操作,且其方法调用都是同步的,程序流需要等到 sockets 处理完 I/O 才能执行,不支持异步
Jedis 在实现上是直接连接的 redis server,如果在多线程环境下是非线程安全的,这个时候可以使用连接池来管理 Jedis,解决 Jedis 客户端实例存在非线程安全的问题(也就是可以通过配置JedisPool来实现基于Jedis的连接池)
不支持读写分离,需要自己实现
技术文档差,可以说几乎没有
通过配置 JedisPool 设置连接池并将JedisPool对象注入到spring容器内,使用时通过 @Autowired 方式注入JedisPool 使用。
示例:
pom文件
<!--jedis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>4.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok 因为要用到 @Slf4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>package com.lazy.redis;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
@Slf4j
public class JedisDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.0.128", 6379);
jedis.auth("redis");
log.info("redis 连接成功");
log.info("ping,{}", jedis.ping());
//string
log.info("-------string---------");
jedis.set("k1", "v1");
System.out.println(jedis.get("k1"));
//list
log.info("-------list---------");
jedis.lpush("list", "3", "2", "3", "4", "5");
List<String> list = jedis.lrange("list", 0, -1);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
//set
log.info("----------set----------");
jedis.sadd("orders", "1");
jedis.sadd("orders", "2");
jedis.sadd("orders", "3");
Set<String> orders = jedis.smembers("orders");
orders.forEach(System.out::println);
jedis.srem("orders", "1");
//打印orders
log.info("orders,size:{}", jedis.smembers("orders").size());
//hash
log.info("----------hash----------");
jedis.hset("hash1", "userName", "zs");
log.info("hash:{}", jedis.hget("hash1", "userName"));
HashMap<String, String> hash2 = new HashMap<>();
hash2.put("userName", "zs");
hash2.put("age", "20");
hash2.put("email", "@qq.com");
jedis.hmset("hash2", hash2);
//打印 hash2的值
log.info("-----hash2-----");
List<String> hmget = jedis.hmget("hash2", "userName", "age", "email");
hmget.forEach(System.out::println);
log.info("-----zset-----");
//zset
jedis.zadd("zset01", 50d, "70");
jedis.zadd("zset01", 60d, "90");
jedis.zadd("zset01", 70d, "70");
List<String> zset01 = jedis.zrange("zset01", 0, -1);
zset01.forEach(System.out::println);
jedis.flushDB();
//关闭连接
jedis.close();
}
}Lettuce
Lettuce是一个Redis的Java驱动包,Lettuce翻译为生菜,没错,就是吃的那种生菜,所以它的Logo长这样

Lettuce 是一种可扩展的、线程安全的 Redis 高级客户端,从 Spring Boot 2.x 开始, Lettuce 已取代 Jedis 成为SpringBoot 默认的 Redis 客户端 优点:
- 相比于 Jedis,Lettuce 属于后起之秀,对 Redis 支持更加全面,并且解决了 Jedis 客户端实例存在非线程安全的问题
- 支持同步编程,异步编程,响应式编程,自动重新连接,主从模式,集群模块,哨兵模式,管道和编码器等等高级的 Redis 特性
- Lettuce 底层基于 Netty 框架的事件驱动与 redis 通信,采用了非阻塞的 I/O 操作,可异步调用,相比 Jedis,性能高
- Letuce 的 API 是线程安全的,如果不是执行阻塞和事务操作,如 BLPOP 和MULTI/EXEC 等命令,多个线程就可以共享一个连接,性能方面差异很小
缺点:
- API 更加抽象,学习使用成本高
RedisTemplate是Spring Data Redis框架提供的对Jedis和Lettuce的封装客户端,本质上还是使用Jedis或Lettuce,spring boot1.x的版本默认采用Jedis实现,spring boot2.x的版本默认采用Lettuce实现;可以方便的在Jedis和Lettuce之间切换具体的客户端实现;和日志门面与日志实现框架的关系一样,日志门面统一了操作日志的api,而具体日志的记录交给日志实现框去做,这样在切换日志实现时不用修改日志相关代码;RedisTemplate性能上不及Jedis,使用RedisTemplate时项目中至少需要有Jedis或Lettuce客户端之一的依赖包,否则会报错,RedisTemplate会自动根据项目中依赖的客户端选择底层使用Jedis还是Lettuce。
Jedis和Lettuce的区别
jedis和Lettuce都是Redis的客户端,它们都可以连接Redis服务器,但是在SpringBoot2.0之后默认都是使用的 Lettuce 这个客户端连接Redis服务器,因为当时使用Jedis客户端连接Redis 服务器的时候,每个线程都要拿自己创建的Jedis实例去连接Redis客户端,当有很多个线程的时候,不仅开销大需要反复的创建关闭一个Jedis连接,而且也是线程不安全的,一个线程通过Jedis实例更改Redis服务器中的数据之后会影响另一个线程。
但是如果使用 Lettuce 这个客户端连接 Redis 服务器的时候,就不会出现上面的情况,Lettuce 底层使用的是 Netty,当有多个线程都需要连接 Redis 服务器的时候,可以保证只创建一个 Lettuce 连接,使所有的线程共享这一个 Lettuce 连接,这样可以减少创建关闭一个 Lettuce 连接时候的开销;而且这种方式也是线程安全的,不会出现一个线程通过 Lettuce 更改 Redis 服务器中的数据之后而影响另一个线程的情况;
使用:
pom
<dependency>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
<version>6.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>package com.lazy.redis;
import io.lettuce.core.RedisClient;
import io.lettuce.core.RedisURI;
import io.lettuce.core.SortArgs;
import io.lettuce.core.api.StatefulRedisConnection;
import io.lettuce.core.api.sync.RedisCommands;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
@Slf4j
public class LettuceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用构建器链式编程 构建 RedisURI.builder
RedisURI uri = RedisURI.Builder
.redis("192.168.0.128")
.withPort(6379)
.withAuthentication("default", "redis")
.build();
//创建连接 redis 客户端
RedisClient redisClient = RedisClient.create(uri);
//创建连接
StatefulRedisConnection<String, String> connect = redisClient.connect();
//创建redis同步操作命令
RedisCommands<String, String> commands = connect.sync();
//string
log.info("=======string======");
commands.set("k1","v1");
log.info("string:{}",commands.get("k1"));
//list
log.info("========list=========");
commands.lpush("list","1","2","3","4","5");
List<String> list = commands.lrange("list", 0, -1);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
log.info("=======set=======");
commands.sadd("set","set1","set2","set3");
Set<String> set = commands.smembers("set");
set.forEach(System.out::println);
log.info("=======hash=======");
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("k1", "v1");
hashMap.put("k2", "v2");
hashMap.put("k3", "v3");
commands.hset("hash",hashMap);
Map<String, String> hash = commands.hgetall("hash");
hash.keySet().forEach(System.out::println);
log.info("=======zset=======");
commands.zadd("zset",20d,"20");
commands.zadd("zset",30d,"30");
commands.zadd("zset",60d,"60");
List<String> zset = commands.zrange("zset", 0, -1);
zset.forEach(System.out::println);
//关闭资源
redisClient.shutdown();
redisClient.close();
}
}RedisTemplate
pom
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- swagger3 OpenAPI -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>yaml
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: Redis7_study
swagger2:
enable: true # 是否开启swagger
data:
redis:
host: 192.168.0.128 # redis IP 地址
database: 0 # redis 0号数据库
port: 6379 # redis 端口
password: redis # redis 密码
lettuce:
pool: # lettuce 连接池
max-active: 8 # 连接池最大连接数
max-wait: -1ms # 连接池最大阻塞等待
max-idle: 8 # 连接池最大空闲连接
min-idle: 0 # 连接池最小空闲连接service
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderService {
private final String ORDER_KEY = "order:";
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public void addOrder(){
int keyId = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100) + 1;
String order_id = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
String key = ORDER_KEY + keyId;
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "京东订单:"+order_id);
log.info("*****京东订单已生成:编号{},订单号{}",key,order_id);
}
public String getOrder(){
return (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(ORDER_KEY);
}
}controller
@RestController
@Slf4j
@Tag(name = "订单接口")
public class OrderController {
@Resource
private OrderService orderService;
@PostMapping("/order/add")
@Operation(summary = "新增订单")
public void addOrder() {
orderService.addOrder();
}
@GetMapping("/order/getOder/{orderId}")
@Operation(summary = "根据order获取订单")
public void getOrder(@PathVariable("orderId") String orderId) {
orderService.getOrder();
}
}启动运行
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/index.html
测试 addOrder

发现乱码,明明启动的时候已经添加了,解析中文的命令了,怎么还会乱码?
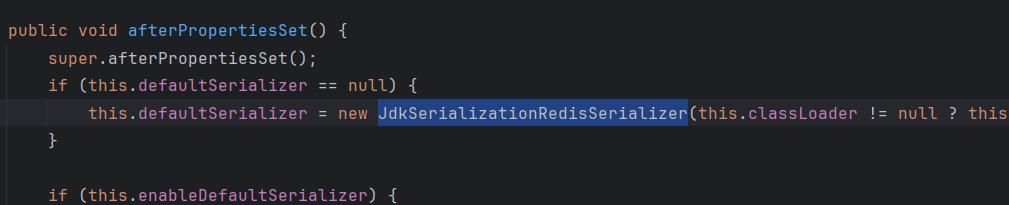
阅读RedisTemplate源码后发现,默认情况下,RedisTemplate 使用该数据列化方式,我们来看下源码 RedisTemplate#afterPropertiesSet()
解决方法
不用
RedisTemplate改用StringRedisTemplateorderService
java@Service @Slf4j public class OrderService { private final String ORDER_KEY = "order:"; @Resource private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; public void addOrder(){ int keyId = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100) + 1; String order_id = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", ""); String key = ORDER_KEY + keyId; stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, order_id); log.info("*****京东订单已生成:编号{},订单号{}",key,order_id); } public String getOrder(){ return stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(ORDER_KEY); } }在测试一下
发现没有问题
继续使用
RedisTemplate,添加RedisConfig在RedisConfig里面 去指定序列化方式
javapackage com.lazy.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; @Configuration public class RedisConfig { /** * redis序列化的工具配置类,下面这个请一定开启配置 * 127.0.0.1:6379> keys * * 1) "ord:102" 序列化过 * 2) "\xac\xed\x00\x05t\x00\aord:102" 野生,没有序列化过 * this.redisTemplate.opsForValue(); //提供了操作string类型的所有方法 * this.redisTemplate.opsForList(); // 提供了操作list类型的所有方法 * this.redisTemplate.opsForSet(); //提供了操作set的所有方法 * this.redisTemplate.opsForHash(); //提供了操作hash表的所有方法 * this.redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); //提供了操作zset的所有方法 * @param lettuceConnectionFactory * @return */ @Bean public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory) { RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>(); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(lettuceConnectionFactory); //设置key序列化方式string redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); //设置value的序列化方式json,使用GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer替换默认序列化 redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()); redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()); redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet(); return redisTemplate; } }测试
也没有问题
getOder
连接redis注意:
- bind 配置请注释掉
- 保护模式设置为no
- linux 系统的防火墙设置
- redis服务器的IP和密码是否正确
- 忘记写访问redis的服务端口号和密码
- slave-read-only 设置成no 要不然服务器没有读写权限
Spring集成RedisTemplate集群
启动redis集6台实例
添加集群yaml
yamlserver: port: 8080 spring: application: name: Redis7_study swagger2: enable: true # 是否开启swagger data: redis: host: 192.168.0.128 # redis IP 地址 database: 0 # redis 0号数据库 port: 6379 # redis 端口 password: redis # redis 密码 lettuce: pool: # lettuce 连接池 max-active: 8 # 连接池最大连接数 max-wait: -1ms # 连接池最大阻塞等待 max-idle: 8 # 连接池最大空闲连接 min-idle: 0 # 连接池最小空闲连接 cluster: # 添加集群 nodes: 192.168.0.128:6381,192.168.0.128:6382,192.168.0.128:6383,192.168.0.128:6384,192.168.0.128:6385,192.168.0.128:6386启动测试

添加成功
问题 SpringBoot2出现的问题
人为模拟,master-6381机器意外宕机,手动shutdown
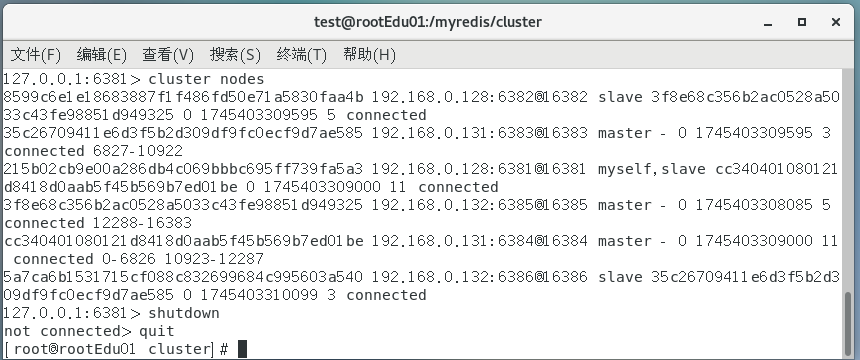
在对redis集群命令方式,手动验证各种读写命令,看看6384是否上位
- 6384已经上位了
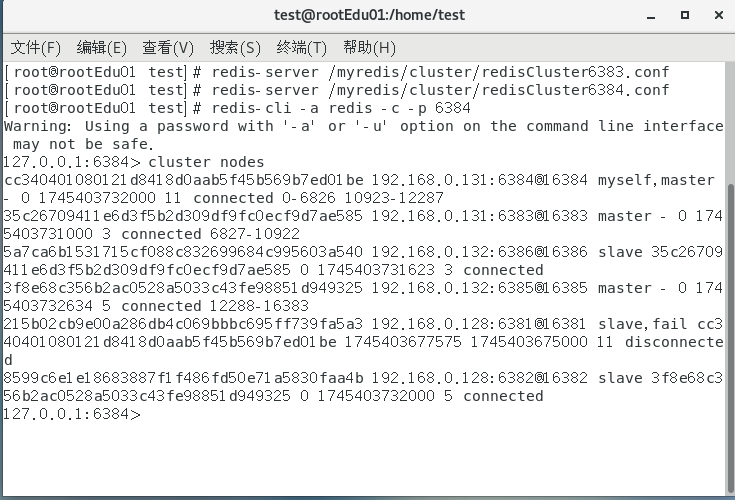
Redis Cluster 集群能自动感知并自动完成主备切换,对应的slave6384会被选举出新的master节点
微服务客户端再次读写访问试试
Redis Cluster集群部署采用了3主3从拓扑结构,数据读写访问master节点, slave节点负责备份。当master宕机主从切换成功,redis手动OK,but 2个经典故障
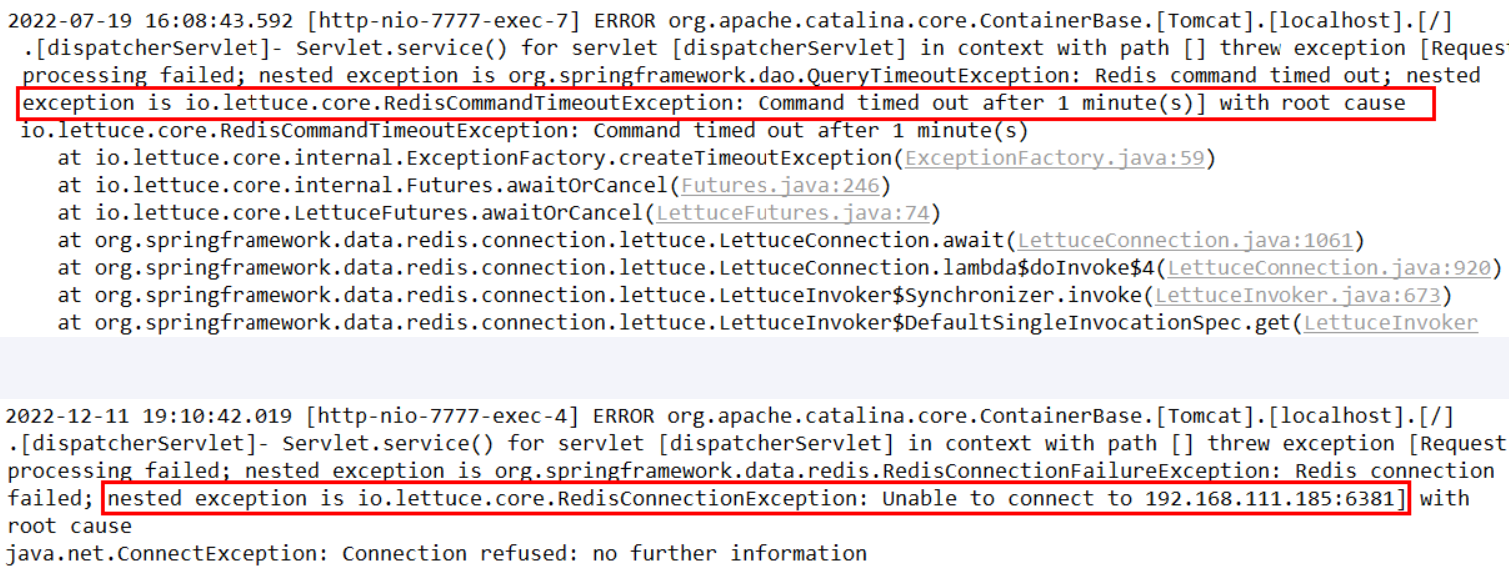
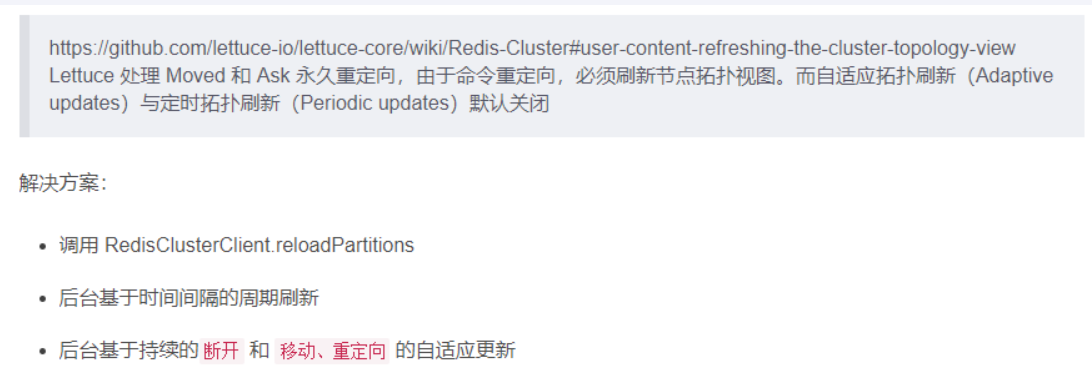
SpringBoot 2.X 版本,Redis 默认的连接池采用 Lettuce 当 Redis集群节点发生变化后,Lettuce 默认是不会刷新节点拓扑
解决方案
排除 Lettuce 采用 Jedis(不推荐)
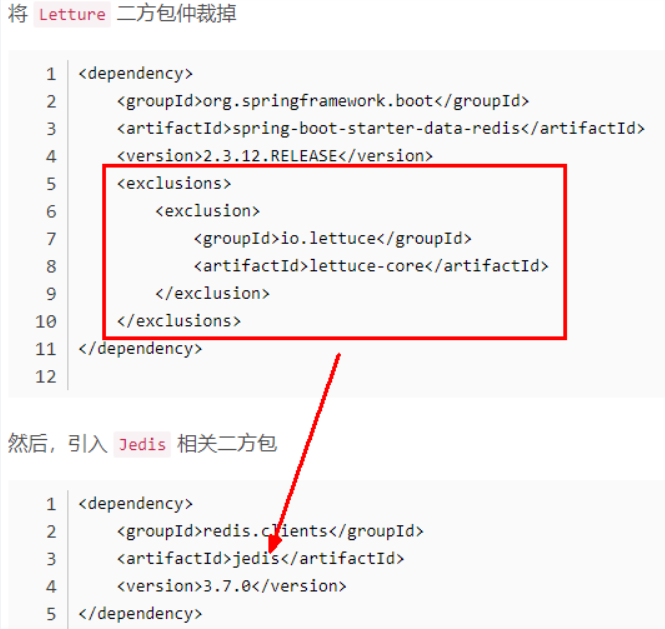
重写连接工厂实例(极度不推荐)
java@Bean public DefaultClientResources lettuceClientResources() { return DefaultClientResources.create(); } @Bean public LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory(RedisProperties redisProperties, ClientResources clientResources) { ClusterTopologyRefreshOptions topologyRefreshOptions = ClusterTopologyRefreshOptions.builder() .enablePeriodicRefresh(Duration.ofSeconds(30)) //按照周期刷新拓扑 .enableAllAdaptiveRefreshTriggers() //根据事件刷新拓扑 .build(); ClusterClientOptions clusterClientOptions = ClusterClientOptions.builder() //redis命令超时时间,超时后才会使用新的拓扑信息重新建立连 .timeoutOptions(TimeoutOptions.enabled(Duration.ofSeconds(10))) .topologyRefreshOptions(topologyRefreshOptions) .build(); LettuceClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = LettuceClientConfiguration.builder() .clientResources(clientResources) .clientOptions(clusterClientOptions) .build(); RedisClusterConfiguration clusterConfig = new RedisClusterConfiguration(redisProperties.getCluster().getNodes()); clusterConfig.setMaxRedirects(redisProperties.getCluster().getMaxRedirects()); clusterConfig.setPassword(RedisPassword.of(redisProperties.getPassword())); LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory = new LettuceConnectionFactory(clusterConfig, clientConfiguration); return lettuceConnectionFactory; }刷新节点集群拓扑动态感应
改写yaml
yamlserver: port: 8080 spring: application: name: Redis7_study swagger2: enable: true # 是否开启swagger data: redis: host: 192.168.0.128 # redis IP 地址 database: 0 # redis 0号数据库 port: 6379 # redis 端口 password: redis # redis 密码 lettuce: pool: # lettuce 连接池 max-active: 8 # 连接池最大连接数 max-wait: -1ms # 连接池最大阻塞等待 max-idle: 8 # 连接池最大空闲连接 min-idle: 0 # 连接池最小空闲连接 cluster: # 添加集群 nodes: 192.168.0.128:6381,192.168.0.128:6382,192.168.0.128:6383,192.168.0.128:6384,192.168.0.128:6385,192.168.0.128:6386 refresh: period: 2000 # 定时刷新 refresh: adaptive: true #支持集群拓扑动态感应刷新,自适应拓扑刷新是否使用所有可用的更新,默认false关闭